Evaluation of pure ground glass pulmonary nodule: a case report
- PMID: 25317265
- PMCID: PMC4185143
- DOI: 10.3402/jchimp.v4.24562
Evaluation of pure ground glass pulmonary nodule: a case report
Abstract
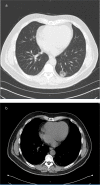
A pulmonary nodule is a single, nearly spherical, well-circumscribed pulmonary opacity up to 30 mm in diameter and surrounded by aerated lung tissue. In radiographs, pulmonary nodules may appear as solid, completely obscuring the lung parenchyma, or as subsolid, not completely obscuring adjacent tissues. A subsolid pulmonary nodule may be further subclassified as a pure ground glass nodule (pGGN) or a part solid nodule, a mixture of ground glass components and focal opacity obscuring the adjacent tissues. Guidelines for evaluation of solid pulmonary nodules are based on nodule size, recommending vigilance and non-operative management for small nodules (less than 8 mm in diameter) and diagnostic biopsy for nodules with a diameter of 8 mm or more. However, subsolid ground glass pulmonary nodules are an exception to this rule. Although small in size, persistent subsolid nodules are potentially premalignant or malignant. We present the case of a non-smoker who was found to have an incidental pulmonary pGGN. We then discuss the radiologic appearance, histology, clinical outcomes, and evaluation and management strategy of subsolid pulmonary nodules compared with solid nodules.
Keywords: papillary adenocarcinoma; pulmonary nodule; subsolid.
Figures


References
-
- Gould MK, Donington J, Lynch WR, Mazzone PJ, Midthun DE, Naidich DP, et al. Evaluation of individuals with pulmonary nodules: When is it lung cancer? Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2013;143:e93S–120S. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Henschke CI, Yankelevitz DF, Mirtcheva R, McGuinness G, McCauley D, Miettinen OS. CT screening for lung cancer: Frequency and significance of part-solid and nonsolid nodules. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;178:1053–7. - PubMed
-
- Godoy MC, Naidich DP. Overview and strategic management of subsolid pulmonary nodules. J Thorac Imaging. 2012;27:240–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
