Studies on properties of rice straw/polymer nanocomposites based on polycaprolactone and Fe₃O₄ nanoparticles and evaluation of antibacterial activity
- PMID: 25318051
- PMCID: PMC4227226
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms151018466
Studies on properties of rice straw/polymer nanocomposites based on polycaprolactone and Fe₃O₄ nanoparticles and evaluation of antibacterial activity
Abstract
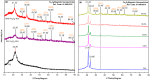
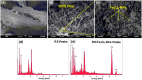
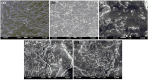
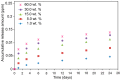
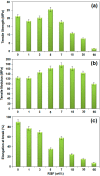
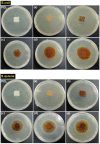
Modified rice straw/Fe3O4/polycaprolactone nanocomposites (ORS/Fe3O4/ PCL-NCs) have been prepared for the first time using a solution casting method. The RS/Fe3O4-NCs were modified with octadecylamine (ODA) as an organic modifier. The prepared NCs were characterized by using X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). The XRD results showed that as the intensity of the peaks decreased with the increase of ORS/Fe3O4-NCs content in comparison with PCL peaks, the Fe3O4-NPs peaks increased from 1.0 to 60.0 wt. %. The TEM and SEM results showed a good dispersion of ORS/Fe3O4-NCs in the PCL matrix and the spherical shape of the NPs. The TGA analysis indicated thermal stability of ORS/Fe3O4-NCs increased after incorporation with PCL but the thermal stability of ORS/Fe3O4/PCL-NCs decreased with the increase of ORS/Fe3O4-NCs content. Tensile strength was improved with the addition of 5.0 wt. % of ORS/Fe3O4-NCs. The antibacterial activities of the ORS/Fe3O4/PCL-NC films were examined against Gram-negative bacteria (Escherichia coli) and Gram-positive bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) by diffusion method using nutrient agar. The results indicated that ORS/Fe3O4/PCL-NC films possessed a strong antibacterial activity with the increase in the percentage of ORS/Fe3O4-NCs in the PCL.
Figures





References
-
- Zhao Q., Tao J., Yam R.C.M., Mok A.C.K., Li R.K.Y., Song C. Biodegradation behavior of polycaprolactone/rice husk ecocomposites in simulated soil medium. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008;93:1571–1576. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2008.05.002. - DOI
-
- García M., Garmendia I., García J. Influence of natural fiber type in eco-composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008;107:2994–3004. doi: 10.1002/app.27519. - DOI
-
- Wu C.-S., Liao H.-T. Polycaprolactone-Based Green Renewable Ecocomposites Made from Rice Straw Fiber: Characterization and Assessment of Mechanical and Thermal Properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012;51:3329–3337. doi: 10.1021/ie202002p. - DOI
-
- Mohanty A.K., Misra M., Drzal L.T. Sustainable Bio-Composites from Renewable Resources: Opportunities and Challenges in the Green Materials World. J. Polym. Environ. 2002;10:19–26. doi: 10.1023/A:1021013921916. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

