Hive-stored pollen of honey bees: many lines of evidence are consistent with pollen preservation, not nutrient conversion
- PMID: 25319366
- PMCID: PMC4285803
- DOI: 10.1111/mec.12966
Hive-stored pollen of honey bees: many lines of evidence are consistent with pollen preservation, not nutrient conversion
Erratum in
- Mol Ecol. 2015 Feb;24(3):698. Lanan, Michele C [added]
Abstract
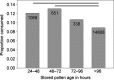
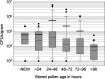
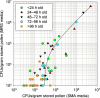
Honey bee hives are filled with stored pollen, honey, plant resins and wax, all antimicrobial to differing degrees. Stored pollen is the nutritionally rich currency used for colony growth and consists of 40-50% simple sugars. Many studies speculate that prior to consumption by bees, stored pollen undergoes long-term nutrient conversion, becoming more nutritious 'bee bread' as microbes predigest the pollen. We quantified both structural and functional aspects associated with this hypothesis using behavioural assays, bacterial plate counts, microscopy and 454 amplicon sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene from both newly collected and hive-stored pollen. We found that bees preferentially consume fresh pollen stored for <3 days. Newly collected pollen contained few bacteria, values which decreased significantly as pollen were stored >96 h. The estimated microbe to pollen grain surface area ratio was 1:1 000 000 indicating a negligible effect of microbial metabolism on hive-stored pollen. Consistent with these findings, hive-stored pollen grains did not appear compromised according to microscopy. Based on year round 454 amplicon sequencing, bacterial communities of newly collected and hive-stored pollen did not differ, indicating the lack of an emergent microbial community co-evolved to digest stored pollen. In accord with previous culturing and 16S cloning, acid resistant and osmotolerant bacteria like Lactobacillus kunkeei were found in greatest abundance in stored pollen, consistent with the harsh character of this microenvironment. We conclude that stored pollen is not evolved for microbially mediated nutrient conversion, but is a preservative environment due primarily to added honey, nectar, bee secretions and properties of pollen itself.
Keywords: Lactobacillus kunkeei; bee bread; fermentation; honey; microbes; nutrition.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Ahn J-H, Hong I-P, Bok J-I, et al. Pyrosequencing analysis of the bacterial communities in the guts of honey bees Apis cerana and Apis mellifera in Korea. Journal of Microbiology. 2012;50:735–745. - PubMed
-
- Aleklett K, Hart M, Shade A. The microbial ecology of flowers: an emerging frontier in phyllosphere research. Botany-Botanique. 2014;92:253–266.
-
- Alvarez-Pérez S, Herrera CM, de Vega C. Zooming-in on floral nectar: a first exploration of nectar-associated bacteria in wild plant communities. FEMS Microbiology Ecology. 2012;80:591–602. - PubMed
-
- Amdam GV, Omholt SW. The regulatory anatomy of honeybee lifespan. Journal of Theoretical Biology. 2002;216:209–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

