Peritoneal surface disease (PSD) from appendiceal cancer treated with cytoreductive surgery (CRS) and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC): overview of 481 cases
- PMID: 25319583
- PMCID: PMC4346452
- DOI: 10.1245/s10434-014-4147-y
Peritoneal surface disease (PSD) from appendiceal cancer treated with cytoreductive surgery (CRS) and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC): overview of 481 cases
Abstract
Background: Cytoreductive surgery (CRS) and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) used to treat peritoneal surface disease (PSD) from appendiceal cancer have shown variability in survival outcomes. The primary goal of this study was to determine predictors of surgical morbidity and overall survival. The secondary goal was to describe the impact of nodal status on survival after CRS/HIPEC for PSD from low-grade appendiceal (LGA) and high-grade appendiceal (HGA) primary lesions.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of 1,069 procedures from a prospective database was performed. Patient characteristics, tumor grade, nodal status, performance status, resection status, morbidity, mortality, and survival were reviewed.
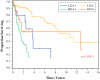
Results: The study identified 481 CRS/HIPEC procedures: 317 (77.3 %) for LGA and 93 (22.7 %) for HGA lesions. The median follow-up period was 44.4 months, and the 30-day major morbidity and mortality rates were respectively 27.8 and 2.7 %. Major morbidity was jointly predicted by incomplete cytoreduction (p = 0.0037), involved nodes (p < 0.0001), and comorbidities (p = 0.003). Multivariate negative predictors of survival included positive nodal status (p = 0.003), incomplete cytoreduction (p < 0.0001), and preoperative chemotherapy (p = 0.04) in LGA patients and incomplete cytoreduction (p = 0.0003) and preoperative chemotherapy (p = 0.0064) in HGA patients. After complete cytoreduction, median survival was worse for patients with positive nodes than for those with negative nodes in LGA (85 months vs not reached [82 % alive at 90 months]; p = 0.002) and HGA (30 vs 153 months; p < 0.0001).
Conclusions: Positive nodes are associated with decreased survival not only for HGA patients but also for LGA patients even after complete cytoreduction. Nodal status further stratifies histologic grade as a prognostic indicator of survival. Patients with node-negative HGA primary lesions who receive a complete cytoreduction may experience survival comparable with that for LGA patients.
Figures

References
-
- Chua TC, Moran BJ, Sugarbaker PH, et al. Early- and long-term outcome data of patients with pseudomyxoma peritonei from appendiceal origin treated by a strategy of cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:2449–56. - PubMed
-
- Elias D, Gilly F, Quenet F, et al. Pseudomyxoma peritonei: a French multicentric study of 301 patients treated with cytoreductive surgery and intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2010;36:456–62. - PubMed
-
- Baratti D, Kusamura S, Nonaka D, et al. Pseudomyxoma peritonei: clinical pathological and biological prognostic factors in patients treated with cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15:526–34. - PubMed
-
- Stewart JHt, Shen P, Russell GB, et al. Appendiceal neoplasms with peritoneal dissemination: outcomes after cytoreductive surgery and intraperitoneal hyperthermic chemotherapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006;13:624–34. - PubMed
-
- Bradley RF, Stewart JHt, Russell GB, et al. Pseudomyxoma peritonei of appendiceal origin: a clinicopathologic analysis of 101 patients uniformly treated at a single institution, with literature review. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006;30:551–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

