Resting-state functional connectivity changes in aging apoE4 and apoE-KO mice
- PMID: 25319693
- PMCID: PMC6705289
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0684-14.2014
Resting-state functional connectivity changes in aging apoE4 and apoE-KO mice
Abstract
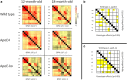
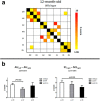
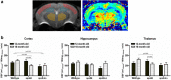
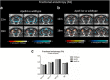
It is well established that the cholesterol-transporter apolipoprotein ε (APOE) genotype is associated with the risk of developing neurodegenerative diseases. Recently, brain functional connectivity (FC) in apoE-ε4 carriers has been investigated by means of resting-state fMRI, showing a marked differentiation in several functional networks at different ages compared with carriers of other apoE isoforms. The causes of such hampered FC are not understood. We hypothesize that vascular function and synaptic repair processes, which are both impaired in carriers of ε4, are the major contributors to the loss of FC during aging. To test this hypothesis, we integrated several different MRI techniques with immunohistochemistry and investigated FC changes in relation with perfusion, diffusion, and synaptic density in apoE4 and apoE-knock-out (KO) mice at 12 (adult) and 18 months of age. Compared with wild-type mice, we detected FC deficits in both adult and old apoE4 and apoE-KO mice. In apoE4 mice, these changes occurred concomitant with increased mean diffusivity in the hippocampus, whereas perfusion deficits appear only later in life, together with reduced postsynaptic density levels. Instead, in apoE-KO mice FC deficits were mirrored by strongly reduced brain perfusion since adulthood. In conclusion, we provide new evidence for a relation between apoE and brain connectivity, possibly mediated by vascular risk factors and by the efficiency of APOE as synaptic modulator in the brain. Our results show that multimodal MR neuroimaging is an excellent tool to assess brain function and to investigate early neuropathology and aging effects in translational research.
Keywords: apoE; apoE4 mice; cerebral blood flow; diffusion tensor imaging; functional connectivity; resting-state fMRI.
Copyright © 2014 the authors 0270-6474/14/3413963-13$15.00/0.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
