Vigorous physical activity impairs myocardial function in patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy and in mutation positive family members
- PMID: 25319773
- PMCID: PMC4278531
- DOI: 10.1002/ejhf.181
Vigorous physical activity impairs myocardial function in patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy and in mutation positive family members
Abstract
Aims: Exercise increases risk of ventricular arrhythmia in subjects with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC). We aimed to investigate the impact of exercise on myocardial function in ARVC subjects.
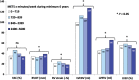
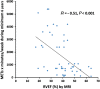
Methods and results: We included 110 subjects (age 42 ± 17 years), 65 ARVC patients and 45 mutation-positive family members. Athletes were defined as subjects with ≥4 h vigorous exercise/week [≥1440 metabolic equivalents (METs × minutes/week)] during a minimum of 6 years. Athlete definition was fulfilled in 37/110 (34%) subjects. We assessed right ventricular (RV) and left ventricular (LV) myocardial function by echocardiography, and by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The RV function by RV fractional area change (FAC), RV global longitudinal strain (GLS) by echocardiography, and RV ejection fraction (EF) by MRI was reduced in athletes compared with non-athletes (FAC 34 ± 9% vs. 40 ± 11%, RVGLS -18.3 ± 6.1% vs. -22.0 ± 4.8%, RVEF 32 ± 8% vs. 43 ± 10%, all P < 0.01). LV function by LVEF and LVGLS was reduced in athletes compared with non-athletes (LVEF by echocardiography 50 ± 10% vs. 57 ± 5%, LVEF by MRI 46 ± 6% vs. 53 ± 8%, and LVGLS -16.7 ± 4.2% vs. -19.4 ± 2.9%, all P < 0.01). The METs × minutes/week correlated with reduced RV and LV function by echocardiography and MRI (all P < 0.01). The LVEF by MRI was also reduced in subgroups of athlete index patients (46 ± 7% vs. 54 ± 10%, P = 0.02) and in athlete family members (47 ± 3% vs. 52 ± 6%, P < 0.05).
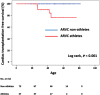
Conclusion: Athletes showed reduced biventricular function compared with non-athletes in ARVC patients and in mutation-positive family members. The amount and intensity of exercise activity was associated with impaired LV and RV function. Exercise may aggravate and accelerate myocardial dysfunction in ARVC.
Keywords: Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy; Exercise; Heart failure; Myocardial function; Ventricular arrhythmia.
© 2014 The Authors. European Journal of Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Defining the interaction between exercise and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy.Eur J Heart Fail. 2015 Feb;17(2):128-31. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.224. Epub 2014 Dec 31. Eur J Heart Fail. 2015. PMID: 25557220 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sen-Chowdhry S, Morgan RD, Chambers JC, McKenna WJ. Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy: etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Annu Rev Med. 2010;61:233–253. - PubMed
-
- Haskell WL, Lee IM, Pate RR, Powell KE, Blair SN, Franklin BA, Macera CA, Heath GW, Thompson PD, Bauman A. Physical activity and public health: updated recommendation for adults from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2007;116:1081–1093. - PubMed
-
- Strath SJ, Kaminsky LA, Ainsworth BE, Ekelund U, Freedson PS, Gary RA, Richardson CR, Smith DT, Swartz AM. Guide to the assessment of physical activity: clinical and research applications: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2013;128:2259–2279. - PubMed
-
- James CA, Bhonsale A, Tichnell C, Murray B, Russell SD, Tandri H, Tedford RJ, Judge DP, Calkins H. Exercise increases age-related penetrance and arrhythmic risk in arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy-associated desmosomal mutation carriers. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:1290–1297. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Corrado D, Basso C, Rizzoli G, Schiavon M, Thiene G. Does sports activity enhance the risk of sudden death in adolescents and young adults? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;42:1959–1963. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

