KRIT1 protein depletion modifies endothelial cell behavior via increased vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling
- PMID: 25320085
- PMCID: PMC4239650
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.582304
KRIT1 protein depletion modifies endothelial cell behavior via increased vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling
Abstract
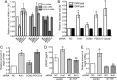
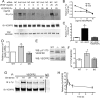
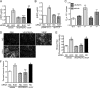
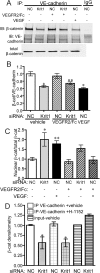
Disruption of endothelial cell-cell contact is a key event in many cardiovascular diseases and a characteristic of pathologically activated vascular endothelium. The CCM (cerebral cavernous malformation) family of proteins (KRIT1 (Krev-interaction trapped 1), PDCD10, and CCM2) are critical regulators of endothelial cell-cell contact and vascular homeostasis. Here we show novel regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling in KRIT1-depleted endothelial cells. Loss of KRIT1 and PDCD10, but not CCM2, increases nuclear β-catenin signaling and up-regulates VEGF-A protein expression. In KRIT1-depleted cells, increased VEGF-A levels led to increased VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR2) activation and subsequent alteration of cytoskeletal organization, migration, and barrier function and to in vivo endothelial permeability in KRIT1-deficient animals. VEGFR2 activation also increases β-catenin phosphorylation but is only partially responsible for KRIT1 depletion-dependent disruption of cell-cell contacts. Thus, VEGF signaling contributes to modifying endothelial function in KRIT1-deficient cells and microvessel permeability in Krit1(+/-) mice; however, VEGF signaling is likely not the only contributor to disrupted endothelial cell-cell contacts in the absence of KRIT1.
Keywords: Adherens Junction; CCM; Krit1; Permeability; Phosphotyrosine Signaling; Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF); β-Catenin (B-Catenin).
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Wallez Y., Huber P. (2008) Endothelial adherens and tight junctions in vascular homeostasis, inflammation, and angiogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1778, 794–809 - PubMed
-
- Mammoto A., Mammoto T., Kanapathipillai M., Wing Yung C., Jiang E., Jiang A., Lofgren K., Gee E. P., Ingber D. E. (2013) Control of lung vascular permeability and endotoxin-induced pulmonary oedema by changes in extracellular matrix mechanics. Nat. Commun. 4, 1759. - PubMed
-
- Lee Y. C. (2005) The involvement of VEGF in endothelial permeability: a target for anti-inflammatory therapy. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 6, 1124–1130 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

