Precision treatment of distinct molecular subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: ascribing treatment based on the molecular phenotype
- PMID: 25320368
- PMCID: PMC7521674
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0497
Precision treatment of distinct molecular subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: ascribing treatment based on the molecular phenotype
Abstract
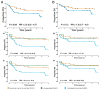
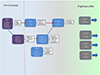
Although diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, was once considered to be a single disease, novel insights into its biology have revealed that it is molecularly heterogeneous. Technologies such as gene expression profiling have revealed that DLBCL consists of at least three distinct molecular diseases that have disparate outcomes following standard therapy. These subtypes arise from different stages of B-cell differentiation and are characterized by distinct oncogenic activation mechanisms. This knowledge has led to the investigation of strategies and novel agents that have selective activity within molecular subtypes and sets the stage for an era of precision medicine in DLBCL therapeutics, where therapy can be ascribed based on molecular phenotype. This work offers the chance of improving the curability of DLBCL, particularly in the activated B-cell subtype, where standard approaches are inadequate for a high proportion of patients. See all articles in this CCR Focus section, "Paradigm Shifts in Lymphoma."
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures


References
-
- Coiffier B, Thieblemont C, Van Den Neste E, Lepeu G, Plantier I, Castaigne S, et al. Long-term outcome of patients in the LNH-98. 5 trial, the first randomized study comparing rituximab-CHOP to standard CHOP chemotherapy in DLBCL patients: a study by the Groupe d’Etudes des Lymphomes de l’Adulte. Blood. 2010;116:2040–5. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shipp MA, Ross KN, Tamayo P, Weng AP, Kutok JL, Aguiar RC, et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma outcome prediction by gene-expression profiling and supervised machine learning. Nature Med. 2002;8:68–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

