Simultaneous modulated accelerated radiation therapy for esophageal cancer: a feasibility study
- PMID: 25320535
- PMCID: PMC4194581
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.13973
Simultaneous modulated accelerated radiation therapy for esophageal cancer: a feasibility study
Abstract
Aim: To establish the feasibility of simultaneous modulated accelerated radiation therapy (SMART) in esophageal cancer (EC).
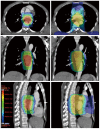
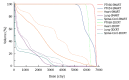
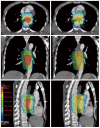
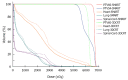
Methods: Computed tomography (CT) datasets of 10 patients with upper or middle thoracic squamous cell EC undergoing chemoradiotherapy were used to generate SMART, conventionally-fractionated three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (3DCRT) and intensity-modulated radiation therapy (cf-IMRT) plans, respectively. The gross target volume (GTV) of the esophagus, positive regional lymph nodes (LN), and suspected lymph nodes (LN ±) were contoured for each patient. The clinical target volume (CTV) was delineated with 2-cm longitudinal and 0.5- to 1.0-cm radial margins with respect to the GTV and with 0.5-cm uniform margins for LN and LN(±). For the SMART plans, there were two planning target volumes (PTVs): PTV66 = (GTV + LN) + 0.5 cm and PTV54 = CTV + 0.5 cm. For the 3DCRT and cf-IMRT plans, there was only a single PTV: PTV60 = CTV + 0.5 cm. The prescribed dose for the SMART plans was 66 Gy/30 F to PTV66 and 54 Gy/30 F to PTV54. The dose prescription to the PTV60 for both the 3DCRT and cf-IMRT plans was set to 60 Gy/30 F. All the plans were generated on the Eclipse 10.0 treatment planning system. Fulfillment of the dose criteria for the PTVs received the highest priority, followed by the spinal cord, heart, and lungs. The dose-volume histograms were compared.
Results: Clinically acceptable plans were achieved for all the SMART, cf-IMRT, and 3DCRT plans. Compared with the 3DCRT plans, the SMART plans increased the dose delivered to the primary tumor (66 Gy vs 60 Gy), with improved sparing of normal tissues in all patients. The Dmax of the spinal cord, V20 of the lungs, and Dmean and V50 of the heart for the SMART and 3DCRT plans were as follows: 38.5 ± 2.0 vs 44.7 ± 0.8 (P = 0.002), 17.1 ± 4.0 vs 25.8 ± 5.0 (P = 0.000), 14.4 ± 7.5 vs 21.4 ± 11.1 (P = 0.000), and 4.9 ± 3.4 vs 12.9 ± 7.6 (P = 0.000), respectively. In contrast to the cf-IMRT plans, the SMART plans permitted a simultaneous dose escalation (6 Gy) to the primary tumor while demonstrating a significant trend of a lower irradiation dose to all organs at risk except the spinal cord, for which no significant difference was found.
Conclusion: SMART offers the potential for a 6 Gy simultaneous escalation in the irradiation dose delivered to the primary tumor of EC and improves the sparing of normal tissues.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01670409.
Keywords: Esophageal cancer; Feasibility; Intensity-modulated radiation therapy; Simultaneous modulated accelerated radiation therapy; Three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Volumetric-modulated arc therapy vs. c-IMRT in esophageal cancer: a treatment planning comparison.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Oct 7;18(37):5266-75. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i37.5266. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23066322 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric comparison of 3DCRT and IMRT in radical chemoradiotherapy of squamous cell carcinoma esophagus.J Cancer Res Ther. 2023 Oct 1;19(7):1844-1851. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.jcrt_1664_21. Epub 2023 Apr 26. J Cancer Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 38376288
-
Simultaneous modulated accelerated radiotherapy in cervical cancer with retroperitoneal lymph node metastasis after radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy.Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2015 Jun;25(5):903-9. doi: 10.1097/IGC.0000000000000426. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25822099
-
Impact of Radiation Dose on Treatment of Maxillary Cancer With Superselective Intra-arterial Cisplatin With Radiotherapy.Anticancer Res. 2023 Jun;43(6):2859-2864. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.16455. Anticancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37247919 Review.
-
Coincidental splenic irradiation and risk of functional hyposplenism in oesophageal cancer treatment.J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2021 Dec;65(7):925-930. doi: 10.1111/1754-9485.13310. Epub 2021 Aug 18. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34405578 Review.
Cited by
-
A phase I/II radiation dose escalation trial using simultaneous integrated boost technique with elective nodal irradiation and concurrent chemotherapy for unresectable esophageal Cancer.Radiat Oncol. 2019 Mar 15;14(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s13014-019-1249-5. Radiat Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30876442 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy versus Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy in Definitive Chemoradiotherapy for Cervical Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Comparison of Survival Outcomes and Toxicities.Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Jan;52(1):31-40. doi: 10.4143/crt.2018.624. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 31048664 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of X-rays and gamma-rays on the mechanical performance of human bone factoring out intraindividual bone structure and composition indices.Mater Today Bio. 2021 Nov 26;13:100169. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2021.100169. eCollection 2022 Jan. Mater Today Bio. 2021. PMID: 34927043 Free PMC article.
-
Different definitions of esophagus influence esophageal toxicity prediction for esophageal cancer patients administered simultaneous integrated boost versus standard-dose radiation therapy.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 9;7(1):120. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00168-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28273921 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation dose escalation by simultaneous modulated accelerated radiotherapy combined with chemotherapy for esophageal cancer: a phase II study.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 19;7(16):22711-9. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8050. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26992206 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Cooper JS, Guo MD, Herskovic A, Macdonald JS, Martenson JA, Al-Sarraf M, Byhardt R, Russell AH, Beitler JJ, Spencer S, et al. Chemoradiotherapy of locally advanced esophageal cancer: long-term follow-up of a prospective randomized trial (RTOG 85-01). Radiation Therapy Oncology Group. JAMA. 1999;281:1623–1627. - PubMed
-
- Minsky BD, Pajak TF, Ginsberg RJ, Pisansky TM, Martenson J, Komaki R, Okawara G, Rosenthal SA, Kelsen DP. INT 0123 (Radiation Therapy Oncology Group 94-05) phase III trial of combined-modality therapy for esophageal cancer: high-dose versus standard-dose radiation therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:1167–1174. - PubMed
-
- Smith TJ, Ryan LM, Douglass HO, Haller DG, Dayal Y, Kirkwood J, Tormey DC, Schutt AJ, Hinson J, Sischy B. Combined chemoradiotherapy vs. radiotherapy alone for early stage squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: a study of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998;42:269–276. - PubMed
-
- Lee N, Harris J, Garden AS, Straube W, Glisson B, Xia P, Bosch W, Morrison WH, Quivey J, Thorstad W, et al. Intensity-modulated radiation therapy with or without chemotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: radiation therapy oncology group phase II trial 0225. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3684–3690. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pollack A, Zagars GK, Starkschall G, Antolak JA, Lee JJ, Huang E, von Eschenbach AC, Kuban DA, Rosen I. Prostate cancer radiation dose response: results of the M. D. Anderson phase III randomized trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;53:1097–1105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

