Long-term outcomes of two rescue therapies in lamivudine-refractory patients with chronic hepatitis B: combined lamivudine and adefovir, and 1-mg entecavir
- PMID: 25320730
- PMCID: PMC4197175
- DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2014.20.3.267
Long-term outcomes of two rescue therapies in lamivudine-refractory patients with chronic hepatitis B: combined lamivudine and adefovir, and 1-mg entecavir
Abstract
Background/aims: Adefovir (ADV) and lamivudine (LAM) combination therapy (ADV+LAM) has been a useful option for patients with LAM-resistant (LAM-r) chronic hepatitis B (CHB). However, the long-term outcomes of LAM+ADV and 1-mg entecavir (ETV) rescue therapies have still been limited. The aim of this study was to determine the long-term outcomes of these two rescue therapies.
Methods: Sixty patients with LAM-r CHB underwent rescue therapy with LAM+ADV (n=36) or 1-mg ETV (n=24). We determined the duration of rescue therapy, timing and type of mutation, undetectable serum hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA by PCR (lower limitation of detection, < 140 copies/mL), biochemical response (alanine aminotransferase < 40 IU/mL), and the incidence of hepatitis B virus e antigen (HBeAg) seroconversion and virologic breakthrough.
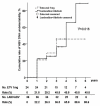
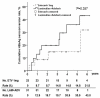
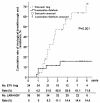
Results: Baseline characteristics did not differ between the two therapy groups. The duration of rescue therapy was 56 months (range, 14-100 months) in the ADV+LAM group and 42 months (range, 12-73 months) in the ETV group (P=0.036). The cumulative rates of HBV DNA undetectability and HBeAg seroconversion up to 6 years were 88.6% and 43.0%, respectively, in the ADV+LAM group, and 45.8% and 31.8% in the ETV group. The rate of virologic breakthrough and resistance was 14.4% in the ADV+LAM group and 71.9% in the ETV group (P=0.001).
Conclusions: Combination of LAM and ADV therapy for up to 6 years achieved modest rates of virological suppression and resistance. ETV is not an optimal therapy because the risk of viral breakthrough to ETV increases over time.
Keywords: Adefovir; Chronic hepatitis B; Entecavir; Lamivudine; Resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Chen CJ, Yang HI, Su J, Jen CL, You SL, Lu SN, et al. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA. 2006;295:65–73. - PubMed
-
- Iloeje UH, Yang HI, Su J, Jen CL, You SL, Chen CJ, et al. Predicting cirrhosis risk based on the level of circulating hepatitis B viral load. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:678–686. - PubMed
-
- Lok AS, McMahon BJ. Chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2007;45:507–539. - PubMed
-
- McMahon BJ. Selecting appropriate management strategies for chronic hepatitis B: who to treat. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101(Suppl 1):S7–S12. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

