Aggressive policing and the mental health of young urban men
- PMID: 25322310
- PMCID: PMC4232139
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2014.302046
Aggressive policing and the mental health of young urban men
Abstract
Objectives: We surveyed young men on their experiences of police encounters and subsequent mental health.
Methods: Between September 2012 and March 2013, we conducted a population-based telephone survey of 1261 young men aged 18 to 26 years in New York City. Respondents reported how many times they were approached by New York Police Department officers, what these encounters entailed, any trauma they attributed to the stops, and their overall anxiety. We analyzed data using cross-sectional regressions.
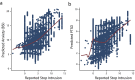
Results: Participants who reported more police contact also reported more trauma and anxiety symptoms, associations tied to how many stops they reported, the intrusiveness of the encounters, and their perceptions of police fairness.
Conclusions: The intensity of respondent experiences and their associated health risks raise serious concerns, suggesting a need to reevaluate officer interactions with the public. Less invasive tactics are needed for suspects who may display mental health symptoms and to reduce any psychological harms to individuals stopped.
Figures
References
-
- Johnson RC, Raphael S. The effects of male incarceration dynamics on acquired immune deficiency syndrome infection rates among African American women and men. J Law Econ. 2009;52(2):251–293.
-
- Western B. Punishment and Inequality in America. New York, NY: Russell Sage Foundation; 2006.
-
- Brame R, Turner MG, Paternoster R, Bushway SD. Cumulative prevalence of arrest from ages 8 to 23 in a national sample. Pediatrics. 2012;129(1):21–27. - PubMed
-
- Kubrin CE, Messner SF, Deanne G, McGeever K, Stucky TD. Proactive policing and robbery rates across US cities. Criminology. 2010;48(1):57–97.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

