Production of salidroside in metabolically engineered Escherichia coli
- PMID: 25323006
- PMCID: PMC4200411
- DOI: 10.1038/srep06640
Production of salidroside in metabolically engineered Escherichia coli
Abstract
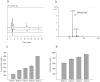
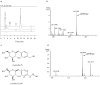
Salidroside (1) is the most important bioactive component of Rhodiola (also called as "Tibetan Ginseng"), which is a valuable medicinal herb exhibiting several adaptogenic properties. Due to the inefficiency of plant extraction and chemical synthesis, the supply of salidroside (1) is currently limited. Herein, we achieved unprecedented biosynthesis of salidroside (1) from glucose in a microorganism. First, the pyruvate decarboxylase ARO10 and endogenous alcohol dehydrogenases were recruited to convert 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate (2), an intermediate of L-tyrosine pathway, to tyrosol (3) in Escherichia coli. Subsequently, tyrosol production was improved by overexpressing the pathway genes, and by eliminating competing pathways and feedback inhibition. Finally, by introducing Rhodiola-derived glycosyltransferase UGT73B6 into the above-mentioned recombinant strain, salidroside (1) was produced with a titer of 56.9 mg/L. Interestingly, the Rhodiola-derived glycosyltransferase, UGT73B6, also catalyzed the attachment of glucose to the phenol position of tyrosol (3) to form icariside D2 (4), which was not reported in any previous literatures.
Conflict of interest statement
This work has been included in a patent application by the Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology.
Figures


References
-
- Ma L. Q. et al. Molecular cloning and overexpression of anovel UDP glucosyltransferase elevating salidroside levels in Rhodiola sachalinensis. Plant Cell Rep 26, 989–999 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Xu J. F., Su Z. G. & Feng P. S. Activity of tyrosol glucosyltransferase and improved salidroside production through biotransformation of tyrosol in Rhodiola sachalinensis cell cultures. J Biotechnol 61, 69–73 (1998).
-
- Yang Y. N. et al. Lignans from the root of Rhodiola crenulata. J Agric Food Chem 60, 964–972 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Mao G. X. et al. Protective role of salidroside against aging in a mouse model induced by D-galactose. Biomed Environ Sci 23, 161–166 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

