Taste receptors in innate immunity
- PMID: 25323130
- PMCID: PMC4286424
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-014-1736-7
Taste receptors in innate immunity
Abstract
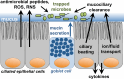
Taste receptors were first identified on the tongue, where they initiate a signaling pathway that communicates information to the brain about the nutrient content or potential toxicity of ingested foods. However, recent research has shown that taste receptors are also expressed in a myriad of other tissues, from the airway and gastrointestinal epithelia to the pancreas and brain. The functions of many of these extraoral taste receptors remain unknown, but emerging evidence suggests that bitter and sweet taste receptors in the airway are important sentinels of innate immunity. This review discusses taste receptor signaling, focusing on the G-protein-coupled receptors that detect bitter, sweet, and savory tastes, followed by an overview of extraoral taste receptors and in-depth discussion of studies demonstrating the roles of taste receptors in airway innate immunity. Future research on extraoral taste receptors has significant potential for identification of novel immune mechanisms and insights into host-pathogen interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Blalock JE. The immune system as the sixth sense. J Intern Med. 2005;257(2):126–138. - PubMed
-
- Blalock JE, Smith EM. Conceptual development of the immune system as a sixth sense. Brain Behav Immun. 2007;21(1):23–33. - PubMed
-
- Bedford FL. The missing sense modality: the immune system. Perception. 2011;40(10):1265–1267. - PubMed
-
- Deckmann K, Filipski K, Krasteva-Christ G, Fronius M, Althaus M, Rafiq A, Papadakis T, Renno L, Jurastow I, Wessels L, Wolff M, Schutz B, Weihe E, Chubanov V, Gudermann T, Klein J, Bschleipfer T, Kummer W. Bitter triggers acetylcholine release from polymodal urethral chemosensory cells and bladder reflexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111(22):8287–8292. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Margolskee RF. Teaching resources. Sensory systems: taste perception. Sci STKE. 2005;290:tr20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

