Function of interleukin-17 and -35 in the blood of patients with hepatitis B-related liver cirrhosis
- PMID: 25323532
- PMCID: PMC4237084
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2681
Function of interleukin-17 and -35 in the blood of patients with hepatitis B-related liver cirrhosis
Abstract
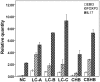
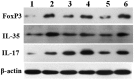
Intrahepatic T helper (Th)17 cytokine and serum interleukin (IL)-17 levels in patients with hepatitis B are positively correlated with the progression of liver cirrhosis (LC). IL-35 can significantly inhibit the differentiation of Th17 cells and the synthesis of IL-17. The present study aimed to investigate the function and expression of IL-17 and IL-35 in the blood of patients with hepatitis B‑related LC. The levels of IL-17 and IL-35 in the peripheral blood of 30 patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB), 79 with LC, 14 with chronic severe hepatitis B (CSHB), and 20 normal controls were detected by ELISA. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction was used to evaluate Epstein-Barr virus-induced gene 3 (EBI3), forkhead box (FOX)P3 and IL-17 mRNA expression levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Western blotting was used to determine protein expression. The liver function of patients and normal controls was measured. EBI3, IL-17 and FOXP3 mRNA expression levels in PBMCs from patients with LC, CHB and CSHB were higher than those in cells from the controls. IL-17 mRNA levels differed significantly according to the Child-Pugh classification and exhibited an upward trend over time in contrast to a downward trend for EBI3 and FOXP3 mRNA. The changes in protein expression in the peripheral blood were consistent with the changes in mRNA expression. Serum IL-17 levels were positively correlated with total bilirubin (TBIL), alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and Child-Pugh grade, and were negatively correlated with albumin. These observed differences were significant. Serum IL-35 levels were negatively correlated with albumin, but not with Child-Pugh grade, ALT and TBIL. IL-17 and IL-35 may be critically involved in the pathogenesis of hepatitis B-related LC.
Figures

References
-
- Wang L, Chen S, Xu K. IL-17 expression is correlated with hepatitis B-related liver diseases and fibrosis. Int J Mol Med. 2011;27:385–392. - PubMed
-
- Liaw YF, Chu CM. Hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet. 2009;373:582–592. - PubMed
-
- Cholongitas E, Papatheodoridis GV, Vangeli M, et al. Systematic review: The model for end-stage liver disease - should it replace Child-Pugh’s classification for assessing prognosis in cirrhosis? Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005;22:1079–1089. - PubMed
-
- Infante-Rivard C, Esnaola S, Villeneuve JP. Clinical and statistical validity of conventional prognostic factors in predicting short-term survival among cirrhotics. Hepatology. 1987;7:660–664. - PubMed
-
- Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, Pietroni MC, Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973;60:646–649. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

