Meteorological conditions related to the onset of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss
- PMID: 25323908
- PMCID: PMC4205711
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.6.1678
Meteorological conditions related to the onset of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss
Abstract
Purpose: The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of meteorological factors on the onset of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSHL).
Materials and methods: Meteorological data from 2005 to 2011 were obtained from the web-based "Monthly Weather Reports of the Meteorological Administration" database. Patients with ISSHL who visited our hospital during this same period and presented the precise day on which hearing loss developed were included in this retrospective study. Twelve meteorological factors were analyzed between the days when ISSHL onset was observed as well as the days when ISSHL did not occur. The weather conditions occurring 1-7 days before ISSHL onset were also analyzed to assess any possible delayed effects of meteorological factors on the onset of ISSHL.
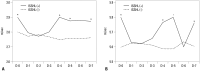
Results: During the study period, 607 patients were included for the study. Although mean and maximal wind velocities were higher for the days when ISSHL occurred than the days without ISSHL onset, after adjusting the value for multiple comparisons, we cannot find any significant relationship between any of meteorological factors and the onset of ISSHL. However, in analysis of time lag effect of the weather conditions, we found that there was still a significant difference in maximum wind speed on 5 days before ISSHL onset even after applying Bonferroni correction.
Conclusion: The result of this study suggests that stronger wind speed may be related to the occurrence of ISSHL.
Keywords: Sudden hearing loss; meteorological factor; wind speed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
REPRINTED FROM THE 2023 HYPERBARIC INDICATIONS MANUAL 15th Edition: Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss.Undersea Hyperb Med. 2024 Fourth Quarter;51(4):425-448. Undersea Hyperb Med. 2024. PMID: 39821771 Review.
-
Labyrinthine artery detection in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss by 7-T MRI.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014 Mar;150(3):455-9. doi: 10.1177/0194599813517990. Epub 2013 Dec 31. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014. PMID: 24381016
-
Effects of meteorological factor and air pollution on sudden sensorineural hearing loss using the health claims data in Busan, Republic of Korea.Am J Otolaryngol. 2019 May-Jun;40(3):393-399. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2019.02.010. Epub 2019 Feb 18. Am J Otolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 30956004
-
Characteristics and prognosis of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss in aged people: a retrospective study.Acta Otolaryngol. 2019 Nov;139(11):959-965. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2019.1657589. Epub 2019 Sep 9. Acta Otolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 31498008
-
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss.Undersea Hyperb Med. 2012 May-Jun;39(3):777-92. Undersea Hyperb Med. 2012. PMID: 22670557 Review.
Cited by
-
Factors Prognostic of Season-Associated Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Retrospective Observational Study.J Audiol Otol. 2017 Apr;21(1):44-48. doi: 10.7874/jao.2017.21.1.44. Epub 2017 Mar 30. J Audiol Otol. 2017. PMID: 28417108 Free PMC article.
-
Association between meteorological factors and audiogram configurations in patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a cross-sectional study.BMJ Open. 2021 Dec 3;11(12):e045768. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-045768. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 34862274 Free PMC article.
-
Air pollution increases the risk of SSNHL: A nested case-control study using meteorological data and national sample cohort data.Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 4;9(1):8270. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44618-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31164673 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated Long-Term Hearing Loss Progression After Recovery From Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss.Front Neurol. 2021 Dec 8;12:738942. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.738942. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34956043 Free PMC article.
-
Association of sudden sensorineural hearing loss with meteorological factors: a time series study in Hefei, China, and a literature review.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Jun;31(30):42970-42990. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-33943-1. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38886269 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shutty MS, Jr, Cundiff G, DeGood DE. Pain complaint and the weather: weather sensitivity and symptom complaints in chronic pain patients. Pain. 1992;49:199–204. - PubMed
-
- Arber N, Vaturi M, Schapiro JM, Jelin N, Weinberger A. Effect of weather conditions on acute gouty arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1994;23:22–24. - PubMed
-
- Jamison RN, Anderson KO, Slater MA. Weather changes and pain: perceived influence of local climate on pain complaint in chronic pain patients. Pain. 1995;61:309–315. - PubMed
-
- Krause I, Shraga I, Molad Y, Guedj D, Weinberger A. Seasons of the year and activity of SLE and Behcet's disease. Scand J Rheumatol. 1997;26:435–439. - PubMed
-
- Bense L. Spontaneous pneumothorax related to falls in atmospheric pressure. Eur J Respir Dis. 1984;65:544–546. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

