A comparison of receptive-expressive language profiles between toddlers with autism spectrum disorder and developmental language delay
- PMID: 25323912
- PMCID: PMC4205715
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.6.1721
A comparison of receptive-expressive language profiles between toddlers with autism spectrum disorder and developmental language delay
Abstract
Purpose: It is well known that expressive language impairment is commonly less severe than receptive language impairment in children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). However, this result is based on experiments in Western countries with Western language scales. This study tries to find whether the result above is applicable for toddlers in a non-Western country; more specifically, in Korea with non-Western language scales.
Materials and methods: The participants were 166 toddlers aged between 20 months and 50 months who visited the clinic from December 2010 to January 2013. The number of toddlers diagnosed as ASD and developmental language delay (DLD) was 103 and 63, respectively. Language development level was assessed using Sequenced Language Scale for Infants (SELSI), a Korean language scale. Using SELSI, each group was divided into 3 sub-groups. Moreover, the group difference by age was observed by dividing them into three age groups. Chi-square test and linear-by-linear association was used for analysis.
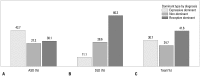
Results: Receptive language ability of the DLD group was superior to that of the ASD group in all age groups. However, expressive language ability in both groups showed no difference in all age groups. A greater proportion of expressive dominant type was found in ASD. The 20-29 months group in ASD showed the largest proportion of expressive language dominant type in the three age groups, suggesting that the younger the ASD toddler is, the more severe the receptive language impairment is.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that receptive-expressive language characteristics in ASD at earlier age could be useful in the early detection of ASD.
Keywords: Autism spectrum disorder; expressive language; receptive language; toddlers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Amer Psychiatric Pub Incorporated. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. Arlington: Amer Psychiatric Pub Incorporated; 2013.
-
- Baranek GT. Autism during infancy: a retrospective video analysis of sensory-motor and social behaviors at 9-12 months of age. J Autism Dev Disord. 1999;29:213–224. - PubMed
-
- De Giacomo A, Fombonne E. Parental recognition of developmental abnormalities in autism. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1998;7:131–136. - PubMed
-
- Maestro S, Muratori F, Barbieri F, Casella C, Cattaneo V, Cavallaro MC, et al. Early behavioral development in autistic children: the first 2 years of life through home movies. Psychopathology. 2001;34:147–152. - PubMed
-
- Clifford SM, Dissanayake C. The early development of joint attention in infants with autistic disorder using home video observations and parental interview. J Autism Dev Disord. 2008;38:791–805. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

