Drugging the undruggable RAS: Mission possible?
- PMID: 25323927
- PMCID: PMC4355017
- DOI: 10.1038/nrd4389
Drugging the undruggable RAS: Mission possible?
Abstract
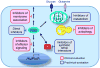
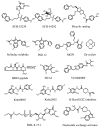
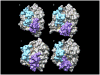
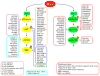
Despite more than three decades of intensive effort, no effective pharmacological inhibitors of the RAS oncoproteins have reached the clinic, prompting the widely held perception that RAS proteins are 'undruggable'. However, recent data from the laboratory and the clinic have renewed our hope for the development of RAS-inhibitory molecules. In this Review, we summarize the progress and the promise of five key approaches. Firstly, we focus on the prospects of using direct inhibitors of RAS. Secondly, we address the issue of whether blocking RAS membrane association is a viable approach. Thirdly, we assess the status of targeting RAS downstream effector signalling, which is arguably the most favourable current approach. Fourthly, we address whether the search for synthetic lethal interactors of mutant RAS still holds promise. Finally, RAS-mediated changes in cell metabolism have recently been described and we discuss whether these changes could be exploited for new therapeutic directions. We conclude with perspectives on how additional complexities, which are not yet fully understood, may affect each of these approaches.
Figures
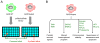
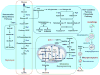
References
-
- Thompson H. US National Cancer Institute’s new Ras project targets an old foe. Nat Med. 2013;19:949–50. - PubMed
-
- Hingorani SR, et al. Trp53R172H and KrasG12D cooperate to promote chromosomal instability and widely metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in mice. Cancer Cell. 2005;7:469–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DP1 CA174419/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA095103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA042978/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 CA148375/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 OD006933/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA175747/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA175747/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA127003/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA179193/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50A095103‑12/PHS HHS/United States
- R01 CA157490/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA179193/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA157490/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- DP1OD006933/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- CA042978/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2CA148375/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DP1CA174419/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

