Effects of AKT inhibition on HGF-mediated erlotinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines
- PMID: 25323938
- PMCID: PMC4562434
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-014-1855-4
Effects of AKT inhibition on HGF-mediated erlotinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines
Abstract
Purpose: Acquired resistance to erlotinib in patients with EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer can result from aberrant activation of alternative receptor tyrosine kinases, such as the HGF-driven c-MET receptor. We sought to determine whether inhibition of AKT signaling could augment erlotinib activity and abrogate HGF-mediated resistance.
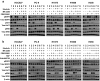
Methods: The effects of MK-2206, a selective AKT inhibitor, were evaluated in combination with erlotinib on a large panel of 13 lung cancer cell lines containing different EGFR or KRAS abnormalities. The activity of the combination was assessed using proliferation assays, flow cytometry and immunoblotting. The MEK inhibitor PD0325901 was used to determine the role of the MAP kinase pathway in erlotinib resistance.
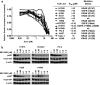
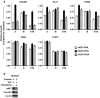
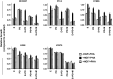
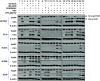
Results: The combination of MK-2206 and erlotinib resulted in synergistic growth inhibition independent of EGFR mutation status. In cell lines where HGF blocked the anti-proliferative and cytotoxic effects of erlotinib, MK-2206 could restore cell cycle arrest, but MEK inhibition was required for erlotinib-dependent apoptosis. Both AKT and MEK inhibition contributed to cell death independent of erlotinib in the T790M-containing H1975 and the EGFR-WT cell lines tested.
Conclusions: These findings illustrate the potential advantages and challenges of combined signal transduction inhibition as a generalized strategy to circumvent acquired erlotinib resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Gandara is a consultant to Merck. Dr. Gandara and Dr. Lara are consultants to Genentech. Dr. Mack has received funding from Merck.
Figures
References
-
- Amann J et al (2005) Aberrant epidermal growth factor receptor signaling and enhanced sensitivity to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Res 65:226–235 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

