hnRNPA1 couples nuclear export and translation of specific mRNAs downstream of FGF-2/S6K2 signalling
- PMID: 25324306
- PMCID: PMC4227786
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku953
hnRNPA1 couples nuclear export and translation of specific mRNAs downstream of FGF-2/S6K2 signalling
Erratum in
-
Correction to 'hnRNPA1 couples nuclear export and translation of specific mRNAs downstream of FGF-2/S6K2 signalling'.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jul 22;52(13):8034. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae525. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38874501 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
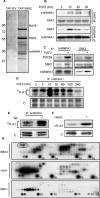
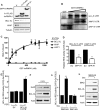
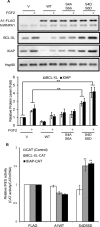
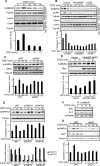
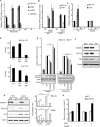
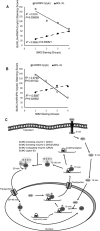
The increased cap-independent translation of anti-apoptotic proteins is involved in the development of drug resistance in lung cancer but signalling events regulating this are poorly understood. Fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF-2) signalling-induced S6 kinase 2 (S6K2) activation is necessary, but the downstream mediator(s) coupling this kinase to the translational response is unknown. Here, we show that S6K2 binds and phosphorylates hnRNPA1 on novel Ser4/6 sites, increasing its association with BCL-XL and XIAP mRNAs to promote their nuclear export. In the cytoplasm, phosphoS4/6-hnRNPA1 dissociates from these mRNAs de-repressing their IRES-mediated translation. This correlates with the phosphorylation-dependent association of hnRNPA1 with 14-3-3 leading to hnRNPA1 sumoylation on K183 and its re-import into the nucleus. A non-phosphorylatible, S4/6A mutant prevented these processes, hindering the pro-survival activity of FGF-2/S6K2 signalling. Interestingly, immunohistochemical staining of lung and breast cancer tissue samples demonstrated that increased S6K2 expression correlates with decreased cytoplasmic hnRNPA1 and increased BCL-XL expression. In short, phosphorylation on novel N-term sites of hnRNPA1 promotes translation of anti-apoptotic proteins and is indispensable for the pro-survival effects of FGF-2.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

References
-
- Li X.H., Li C., Xiao Z.Q. Proteomics for identifying mechanisms and biomarkers of drug resistance in cancer. J. Proteomics. 2011;74:2642–2649. - PubMed
-
- Indran I.R., Tufo G., Pervaiz S., Brenner C. Recent advances in apoptosis, mitochondria and drug resistance in cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2011;1807:735–745. - PubMed
-
- Alama A., Orengo A.M., Ferrini S., Gangemi R. Targeting cancer-initiating cell drug-resistance: a roadmap to a new-generation of cancer therapies. Drug Discov. Today. 2012;17:435–442. - PubMed
-
- Pardo O.E., Arcaro A., Salerno G., Raguz S., Downward J., Seckl M.J. Fibroblast growth factor-2 induces translational regulation of Bcl-XL and Bcl-2 via a MEK-dependent pathway: correlation with resistance to etoposide-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:12040–12046. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

