Factors affecting the health-related quality of life of patients with cervical dystonia and impact of treatment with abobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport): results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study
- PMID: 25324317
- PMCID: PMC4201999
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-005150
Factors affecting the health-related quality of life of patients with cervical dystonia and impact of treatment with abobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport): results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study
Abstract
Objective: To describe the health-related quality of life (HRQOL) burden of cervical dystonia (CD) and report on the HRQOL and patient perception of treatment benefits of abobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport).
Design: The safety and efficacy of a single injection of abobotulinumtoxinA for CD treatment were evaluated in a previously reported international, multicenter, double-blind, randomised trial. HRQOL measures were assessed in the trial and have not been previously reported.
Setting: Movement disorder clinics in the USA and Russia.
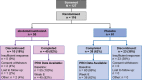
Participants: Patients had to have a diagnosis of CD with symptoms for at least 18 months, as well as a total Toronto Western Spasmodic Torticollis Rating Scale (TWSTRS) score of at least 30; a Severity domain score of at least 15; and a Disability domain score of at least 3. Key exclusion criteria included treatment with botulinum toxin type A (BoNT-A) or botulinum toxin type B (BoNT-B) within 16 weeks of enrolment.
Interventions: Patients were randomised to receive either 500 U abobotulinumtoxinA (n=55) or placebo (n=61).
Primary and secondary outcome measures: Efficacy assessments included TWSTRS total (primary end point) and subscale scores at weeks 0, 4, 8, 12; a pain visual analogue scale at weeks 0 and 4; and HRQOL assessed by the SF-36 Health Survey (SF-36; secondary end point) at weeks 0 and 8.
Results: Patients with CD reported significantly greater impairment for all SF-36 domains relative to US norms. Patients treated with abobotulinumtoxinA reported significantly greater improvements in Physical Functioning, Role Physical, Bodily Pain, General Health and Role Emotional domains than placebo patients (p≤0.03 for all). The TWSTRS was significantly correlated with Physical Functioning, Role Physical and Bodily Pain scores, for those on active treatment.
Conclusions: CD has a marked impact on HRQOL. Treatment with a single abobotulinumtoxinA injection results in significant improvement in patients' HRQOL.
Trial registration number: The trial is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov, numbers NCT00257660 and NCT00288509.
Keywords: QUALITATIVE RESEARCH.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://group.bmj.com/group/rights-licensing/permissions.
Figures
References
-
- Van Zandijcke M. Cervical dystonia (spasmodic torticollis). Some aspects of the natural history. Acta Neurol Belg 1995;95:210–15 - PubMed
-
- Geyer HL, Bressman SB. The diagnosis of dystonia. Lancet Neurol 2006;5:780–90 - PubMed
-
- Kutvonen O, Dastidar P, Nurmikko T. Pain in spasmodic torticollis. Pain 1997;69:279–86 - PubMed
-
- Chan J, Brin MF, Fahn S. Idiopathic cervical dystonia: clinical characteristics. Mov Disord 1991;6:119–26 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical