Impact of familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy-linked mutations in the NH2 terminus of the RLC on β-myosin cross-bridge mechanics
- PMID: 25324513
- PMCID: PMC4269682
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00798.2014
Impact of familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy-linked mutations in the NH2 terminus of the RLC on β-myosin cross-bridge mechanics
Abstract
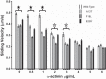
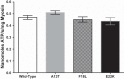
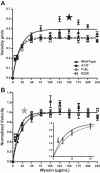
Familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is associated with mutations in sarcomeric proteins, including the myosin regulatory light chain (RLC). Here we studied the impact of three HCM mutations located in the NH2 terminus of the RLC on the molecular mechanism of β-myosin heavy chain (MHC) cross-bridge mechanics using the in vitro motility assay. To generate mutant β-myosin, native RLC was depleted from porcine cardiac MHC and reconstituted with mutant (A13T, F18L, and E22K) or wild-type (WT) human cardiac RLC. We characterized the mutant myosin force and motion generation capability in the presence of a frictional load. Compared with WT, all three mutants exhibited reductions in maximal actin filament velocity when tested under low or no frictional load. The actin-activated ATPase showed no significant difference between WT and HCM-mutant-reconstituted myosins. The decrease in velocity has been attributed to a significantly increased duty cycle, as was measured by the dependence of actin sliding velocity on myosin surface density, for all three mutant myosins. These results demonstrate a mutation-induced alteration in acto-myosin interactions that may contribute to the pathogenesis of HCM.
Keywords: cardiac ventricular myosin; hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; in vitro motility; myosin regulatory light chain.
Copyright © 2014 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Myosin regulatory light chain phosphorylation enhances cardiac β-myosin in vitro motility under load.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015 Aug 15;580:14-21. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2015.06.014. Epub 2015 Jun 25. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015. PMID: 26116789 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiomyopathy-linked myosin regulatory light chain mutations disrupt myosin strain-dependent biochemistry.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Oct 5;107(40):17403-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1009619107. Epub 2010 Sep 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20855589 Free PMC article.
-
E22K mutation of RLC that causes familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in heterozygous mouse myocardium: effect on cross-bridge kinetics.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006 Nov;291(5):H2098-106. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00396.2006. Epub 2006 Jun 2. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16751284
-
Molecular mechanisms of cardiomyopathy phenotypes associated with myosin light chain mutations.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2015 Dec;36(6):433-45. doi: 10.1007/s10974-015-9423-3. Epub 2015 Sep 18. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2015. PMID: 26385864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into human beta-cardiac myosin function from single molecule and single cell studies.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2009 Dec;2(4):426-40. doi: 10.1007/s12265-009-9129-2. Epub 2009 Sep 29. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2009. PMID: 20560001 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy mutations in the pliant and light chain-binding regions of the lever arm of human β-cardiac myosin have divergent effects on myosin function.Elife. 2022 Jun 29;11:e76805. doi: 10.7554/eLife.76805. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35767336 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of myosin light chain-2 (MYL2) in cardiac muscle and disease.Gene. 2015 Sep 10;569(1):14-20. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.06.027. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Gene. 2015. PMID: 26074085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the molecular basis of cardiomyopathy.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022 Feb 1;322(2):H181-H233. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00562.2021. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022. PMID: 34797172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Cardiomyopathy Mutation in the Myosin Essential Light Chain Alters Actomyosin Structure.Biophys J. 2017 Jul 11;113(1):91-100. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2017.05.027. Biophys J. 2017. PMID: 28700929 Free PMC article.
-
Hereditary heart disease: pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and animal models of HCM, RCM, and DCM associated with mutations in cardiac myosin light chains.Pflugers Arch. 2019 May;471(5):683-699. doi: 10.1007/s00424-019-02257-4. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Pflugers Arch. 2019. PMID: 30706179 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chaudoir BM, Kowalczyk PA, Chisholm RL. Regulatory light chain mutations affect myosin motor function and kinetics. J Cell Sci 112: 1611–1620, 1999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

