Adverse effects of 4-tert-octylphenol on the production of oxytocin and hCG in pregnant rats
- PMID: 25324873
- PMCID: PMC4188831
- DOI: 10.5625/lar.2014.30.3.123
Adverse effects of 4-tert-octylphenol on the production of oxytocin and hCG in pregnant rats
Abstract
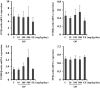
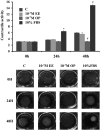
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) are exogenous substances that alter the structure or function of the endocrine system. 4-Tert-octylphenol (OP) is one of the most representative EDCs and has estrogenic effects. In this study, we examined the effects of ethinyl estradiol (EE) and OP on the pituitary gland, placenta, and uterus of pregnant rats. Expression levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), oxytocin (OT), and contraction-associated proteins (CAPs) were determined, and uterine contractile activity was measured by uterine contraction assay. EE and OP both increased mRNA expression of OT and hCG in the pituitary gland but not the placenta. Since OT and hCG control uterine contraction, we next examined CAP expression in the uterus. Expression of 15-hydroxyprostaglandin-dehydrogenase (PGDH) was upregulated by OP, whereas expression of other CAPs was unaffected. To clarify the effect of OP on uterine contraction in pregnant rats, uterine contraction assay was performed. The 17β-Estradiol (E2) did not affect contraction of primary uterine cells harvested from pregnant rats in a 3D collagen gel model. However, OP showed different effects from E2 by significantly reducing contraction activity. In summary, we demonstrated that OP interferes with regulation of OT and hCG in the pituitary gland as well as PGDH in the uterus, thereby reducing uterine contraction activity. This result differs from the action of endogenous E2. Collectively, these findings suggest that exposure to EDCs such as OP during pregnancycan reduce uterine contractile ability, which may result in contraction-associated adverse effects such as metratonia, bradytocia, and uterine leiomyomata.
Keywords: 4-tert-octylphenol; Endocrine-disrupting chemicals; endocrine factors; estradiol; pregnant rats.
Figures

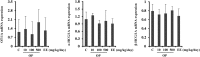
Similar articles
-
Effects of estrogen and estrogenic compounds, 4-tert-octylphenol, and bisphenol A on the uterine contraction and contraction-associated proteins in rats.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013 Aug 15;375(1-2):27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.04.025. Epub 2013 May 7. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23664861
-
The adverse effect of 4-tert-octylphenol on fat metabolism in pregnant rats via regulation of lipogenic proteins.Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2015 Jul;40(1):284-91. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2015.06.020. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26164745
-
Differential effects of octylphenol, 17beta-estradiol, endosulfan, or bisphenol A on the steroidogenic competence of cultured adult rat Leydig cells.Reprod Toxicol. 2001 Sep-Oct;15(5):551-60. doi: 10.1016/s0890-6238(01)00158-7. Reprod Toxicol. 2001. PMID: 11780963
-
Extragonadal gonadotropin receptors, their distribution and function.J Physiol Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;43(4 Suppl 1):33-49. J Physiol Pharmacol. 1992. PMID: 1343973 Review.
-
hCG and Its Disruption by Environmental Contaminants during Human Pregnancy.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 20;19(3):914. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030914. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29558393 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Murine Models and Research Progress on Dysmenorrhea.Reprod Sci. 2023 Aug;30(8):2362-2372. doi: 10.1007/s43032-023-01220-0. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Reprod Sci. 2023. PMID: 37010703 Review.
-
Metabolomics Reveals Metabolic Changes Caused by Low-Dose 4-Tert-Octylphenol in Mice Liver.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 Nov 28;15(12):2686. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15122686. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30487447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nilsson R. Endocrine modulators in the food chain and environment. Toxicol Pathol. 2000;28(3):420–431. - PubMed
-
- White R, Jobling S, Hoare SA, Sumpter JP, Parker MG. Environmentally persistent alkylphenolic compounds are estrogenic. Endocrinology. 1994;135(1):175–182. - PubMed
-
- An BS, Ahn HJ, Kang HS, Jung EM, Yang H, Hong EJ, Jeung EB. Effects of estrogen and estrogenic compounds, 4-tert-octylphenol, and bisphenol A on the uterine contraction and contraction-associated proteins in rats. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013;375(1-2):27–34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

