Prophylactic phenylephrine for iatrogenic priapism: a pilot study with Peyronie's patients
- PMID: 25324950
- PMCID: PMC4198766
- DOI: 10.4111/kju.2014.55.10.665
Prophylactic phenylephrine for iatrogenic priapism: a pilot study with Peyronie's patients
Abstract
Purpose: Although penile duplex Doppler ultrasonography (PDDU) is a common and integral procedure in a Peyronie's disease workup, the intracavernosal injection of vasoactive agents can carry a serious risk of priapism. Risk factors include young age, good baseline erectile function, and no coronary artery disease. In addition, patients with Peyronie's disease undergoing PDDU in an outpatient setting are at increased risk given the inability to predict optimal dosing. The present study was conducted to provide support for a standard protocol of early administration of phenylephrine in patients with a sustained erection after diagnostic intracavernosal injection of vasoactive agents to prevent the deleterious effects of iatrogenic priapism.
Materials and methods: This was a retrospective review of Peyronie's disease patients who received phenylephrine reversal after intracavernosal alprostadil (prostaglandin E1) administration to look at the priapism rate. Safety was determined on the basis of adverse events reported by subjects and efficacy was determined on the basis of the rate of priapism following intervention.
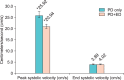
Results: Patients with Peyronie's disease only had better hemodynamic values on PDDU than did patients with Peyronie's disease and erectile dysfunction. All of the patients receiving prophylactic phenylephrine had complete detumescence of erections without adverse events, including no priapism cases.
Conclusions: The reversal of erections with phenylephrine after intracavernosal injections of alprostadil to prevent iatrogenic priapism can be effective without increased adverse effects.
Keywords: Alprostadil; Male urogenital diseases, Peyronie's disease; Phenylephrine; Priapism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Pryor J, Akkus E, Alter G, Jordan G, Lebret T, Levine L, et al. Priapism. J Sex Med. 2004;1:116–120. - PubMed
-
- The European Alprostadil Study Group. The long-term safety of alprostadil (prostaglandin-E1) in patients with erectile dysfunction. Br J Urol. 1998;82:538–543. - PubMed
-
- Coombs PG, Heck M, Guhring P, Narus J, Mulhall JP. A review of outcomes of an intracavernosal injection therapy programme. BJU Int. 2012;110:1787–1791. - PubMed
-
- Domes T, Chung E, DeYoung L, MacLean N, Al-Shaiji T, Brock G. Clinical outcomes of intracavernosal injection in post-prostatectomy patients: a single-center experience. Urology. 2012;79:150–155. - PubMed
-
- Kilic M, Serefoglu EC, Ozdemir AT, Balbay MD. The actual incidence of papaverine-induced priapism in patients with erectile dysfunction following penile colour Doppler ultrasonography. Andrologia. 2010;42:1–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources