Molecular imaging for theranostics in gastroenterology: one stone to kill two birds
- PMID: 25324995
- PMCID: PMC4198552
- DOI: 10.5946/ce.2014.47.5.383
Molecular imaging for theranostics in gastroenterology: one stone to kill two birds
Abstract
Molecular imaging in gastroenterology has become more feasible with recent advances in imaging technology, molecular genetics, and next-generation biochemistry, in addition to advances in endoscopic imaging techniques including magnified high-resolution endoscopy, narrow band imaging or autofluorescence imaging, flexible spectral imaging color enhancement, and confocal laser endomicroscopy. These developments have the potential to serve as "red flag" techniques enabling the earlier and accurate detection of mucosal abnormalities (such as precancerous lesions) beyond biomarkers, virtual histology of detected lesions, and molecular targeted therapy-the strategy of "one stone to kill two or three birds"; however, more effort should be done to be "blue ocean" benefit. This review deals with the introduction of Raman spectroscopy endoscopy, imaging mass spectroscopy, and nanomolecule development for theranostics. Imaging of molecular pathological changes in cells/tissues/organs might open the "royal road" to either convincing diagnosis of diseases that otherwise would only be detected in the advanced stages or novel therapeutic methods targeted to personalized medicine.
Keywords: Imaging mass spectroscopy; Individualized medicine; Molecular imaging; Spectrum analysis, Raman; Theranostics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
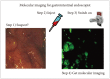
Similar articles
-
Advanced endoscopic imaging: a review of commercially available technologies.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014 Mar;12(3):368-76.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.06.015. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 23811245 Review.
-
Confocal laser endomicroscopy and molecular imaging in barrett esophagus and stomach.Clin Endosc. 2014 Jan;47(1):23-30. doi: 10.5946/ce.2014.47.1.23. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Clin Endosc. 2014. PMID: 24570880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Image-enhanced Endoscopy.Clin Endosc. 2011 Dec;44(2):65-75. doi: 10.5946/ce.2011.44.2.65. Epub 2011 Dec 31. Clin Endosc. 2011. PMID: 22741116 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of New and Emerging Techniques For Optical Diagnosis of Colonic Polyps.J Clin Gastroenterol. 2019 Aug;53(7):495-506. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000001222. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31107294 Review.
-
Cancer risk in IBD: how to diagnose and how to manage DALM and ALM.World J Gastroenterol. 2011 Jul 21;17(27):3184-91. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i27.3184. World J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21912466 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
International digestive endoscopy network 2014: turnpike to the future.Clin Endosc. 2014 Sep;47(5):371-82. doi: 10.5946/ce.2014.47.5.371. Epub 2014 Sep 30. Clin Endosc. 2014. PMID: 25324994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ESR Position Paper on Imaging Biobanks.Insights Imaging. 2015 Aug;6(4):403-10. doi: 10.1007/s13244-015-0409-x. Epub 2015 May 22. Insights Imaging. 2015. PMID: 25999018 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of Raman Spectroscopy as a Probing Tool for Theranostics.Nanotheranostics. 2023 Mar 5;7(3):216-235. doi: 10.7150/ntno.81936. eCollection 2023. Nanotheranostics. 2023. PMID: 37064614 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Miller JC, Thrall JH Commission of Molecular Imaging, American College of Radiology. Clinical molecular imaging. J Am Coll Radiol. 2004;1(1 Suppl):4–23. - PubMed
-
- Rollo FD. Molecular imaging: an overview and clinical applications. Radiol Manage. 2003;25:28–32. - PubMed
-
- Li KC. From molecular imaging to systems diagnostics: time for another paradigm shift? Eur J Radiol. 2009;70:201–204. - PubMed
-
- Badizadegan K, Backman V, Boone CW, et al. Spectroscopic diagnosis and imaging of invisible pre-cancer. Faraday Discuss. 2004;126:265–279. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

