Patterns and predictors of sleep quality before, during, and after hospitalization in older adults
- PMID: 25325580
- PMCID: PMC4265657
- DOI: 10.5664/jcsm.4362
Patterns and predictors of sleep quality before, during, and after hospitalization in older adults
Abstract
Study objectives: The impact of hospitalization on sleep in late-life is underexplored. The current study examined patterns of sleep quality before, during, and following hospitalization, investigated predictors of sleep quality patterns, and examined predictors of classification discordance between two suggested clinical cutoffs used to demarcate poor/good sleep.
Methods: This study included older adults (n = 163; mean age 79.7 ± 6.9 years, 31% female) undergoing inpatient post-acute rehabilitation. Upon admission to inpatient post-acute rehabilitation, patients completed the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) retrospectively regarding their sleep prior to hospitalization. They subsequently completed the PSQI at discharge, and 3 months, 6 months, 9 months, and 1 year post discharge. Patient demographic and clinical characteristics (pain, depression, cognition, comorbidity) were collected upon admission.
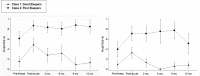
Results: Using latent class analysis methods, older adults could be classified into (1) Consistently Good Sleepers and (2) Chronically Poor Sleepers based on patterns of self-reported sleep quality pre-illness, during, and up to 1 year following inpatient rehabilitation. This pattern was maintained regardless of the clinical cutoff employed (> 5 or > 8). Logistic regression analyses indicated that higher pain and depressive symptoms were consistently associated with an increased likelihood of being classified as a chronic poor sleeper. While there was substantial classification discordance based on clinical cutoff employed, no significant predictors of this discordance emerged.
Conclusions: Clinicians should exercise caution in assessing sleep quality in inpatient settings. Alterations in the cutoffs employed may result in discordant clinical classifications of older adults. Pain and depression warrant detailed considerations when working with older adults on inpatient units when poor sleep is a concern.
Keywords: aging; clinical cutoffs; hospitalization; latent class analysis; sleep.
© 2015 American Academy of Sleep Medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Isaia G, Corsinovi L, Bo M, et al. Insomnia among hospitalized elderly patients: prevalence, clinical characteristics and risk factors. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2011;52:133–7. - PubMed
-
- Drouot X, Cabello B, d'Ortho MP, Brochard L. Sleep in the intensive care unit. Sleep Med Rev. 2008;12:391–403. - PubMed
-
- Foley DJ, Monjan AA, Brown SL, Simonsick EM, Wallace RB, Blazer DG. Sleep complaints among elderly persons: an epidemiological study of three communities. Sleep. 1995;18:425–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical