Comorbidities in infants with obstructive sleep apnea
- PMID: 25325583
- PMCID: PMC4224722
- DOI: 10.5664/jcsm.4204
Comorbidities in infants with obstructive sleep apnea
Abstract
Study objective: The clinical characteristics of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in infants have been insufficiently characterized. Our aim was to describe identifiable comorbidities in infants with obstructive sleep apnea, which may assist in recognizing these patients earlier in their disease course and help improve management.
Methods: This was a single-center, retrospective study involving infants 0-17 months of age with a diagnosis of OSA on the basis of clinical features and nocturnal polysomnography (PSG) at the Mayo Clinic Center for Sleep Medicine between 2000 and 2011. Patients were excluded if they had central apnea accounting for greater than 50% of respiratory events. OSA severity was determined by the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI).
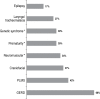
Results: One hundred thirty-nine patients were included. Based upon the AHI, they were subdivided into mild (AHI <5; 30%), moderate (AHI 5-9; 30%), or severe (AHI >10; 40%) categories. Comorbidities included gastroesophageal reflux in 95/139 (68%), periodic limb movements in sleep in 59/139 (42%), craniofacial abnormalities in 52/139 (37%), neuromuscular abnormalities in 47/139 (34%), prematurity in 41/139 (29%), genetic syndromes in 41/139 (29%), laryngomalacia / tracheomalacia in 38/139 (27%), and epilepsy in 23/139 (17%) of subjects. Severity of OSA correlated with prematurity, having a genetic syndrome, or neuromuscular abnormality. Multispecialty evaluation was needed for 119/139 (86%).
Conclusion: Comorbidities in infants with OSA differ from those of older children. Based upon the comorbidities identified in our study population, it appears that appropriate management of infants with OSA requires a multidisciplinary approach involving genetics, gastroenterology, pulmonology, otolaryngology, neurology, and general pediatrics.
Keywords: Infant; obstructive sleep apnea; polysomnography; sleep disordered breathing; sleep disorders.
© 2014 American Academy of Sleep Medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Rosen CL, Larkin EK, Kirchner HL, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for sleep-disordered breathing in 8- to 11-year-old children: association with race and prematurity. J Pediatr. 2003;142:383–9. - PubMed
-
- Emancipator JL, Storfer-Isser A, Taylor HG, et al. Variation of cognition and achievement with sleep-disordered breathing in full-term and preterm children. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2006;160:203–10. - PubMed
-
- Weissbluth M, Davis AT, Poncher J, Reiff J. Signs of airway obstruction during sleep and behavioral, developmental, and academic problems. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 1983;4:119–21. - PubMed
-
- Blunden S, Lushington K, Kennedy D, Martin J, Dawson D. Behavior and neurocognitive performance in children aged 5-10 years who snore compared to controls. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2000;22:554–68. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical