Siderophore-mediated iron acquisition influences motility and is required for full virulence of the xylem-dwelling bacterial phytopathogen Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii
- PMID: 25326304
- PMCID: PMC4272718
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02503-14
Siderophore-mediated iron acquisition influences motility and is required for full virulence of the xylem-dwelling bacterial phytopathogen Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii
Abstract
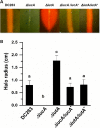
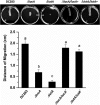
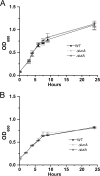
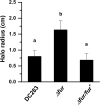
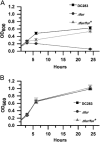
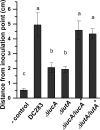
Iron is a key micronutrient for microbial growth but is often present in low concentrations or in biologically unavailable forms. Many microorganisms overcome this challenge by producing siderophores, which are ferric-iron chelating compounds that enable the solubilization and acquisition of iron in a bioactive form. Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii, the causal agent of Stewart's wilt of sweet corn, produces a siderophore under iron-limiting conditions. The proteins involved in the biosynthesis and export of this siderophore are encoded by the iucABCD-iutA operon, which is homologous to the aerobactin biosynthetic gene cluster found in a number of enteric pathogens. Mutations in iucA and iutA resulted in a decrease in surface-based motility that P. stewartii utilizes during the early stages of biofilm formation, indicating that active iron acquisition impacts surface motility for P. stewartii. Furthermore, bacterial movement in planta is also dependent on a functional siderophore biosynthesis and uptake pathway. Most notably, siderophore-mediated iron acquisition is required for full virulence in the sweet corn host, indicating that active iron acquisition is essential for pathogenic fitness for this important xylem-dwelling bacterial pathogen.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The role of Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii leucine-responsive regulatory protein (Lrp) during maize xylem growth.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025 Jul 23;91(7):e0085325. doi: 10.1128/aem.00853-25. Epub 2025 Jun 5. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40470963 Free PMC article.
-
Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii: lessons learned from a xylem-dwelling pathogen of sweet corn.Mol Plant Pathol. 2011 Sep;12(7):628-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2010.00698.x. Epub 2011 Feb 8. Mol Plant Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21726365 Free PMC article.
-
Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii exhibits surface motility, which is a critical aspect of Stewart's wilt disease development on maize.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2008 Oct;21(10):1359-70. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-21-10-1359. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2008. PMID: 18785831
-
Genomics of iron acquisition in the plant pathogen Erwinia amylovora: insights in the biosynthetic pathway of the siderophore desferrioxamine E.Arch Microbiol. 2011 Oct;193(10):693-9. doi: 10.1007/s00203-011-0739-0. Epub 2011 Aug 4. Arch Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21814817 Review.
-
The Ins and Outs of siderophore mediated iron uptake by extra-intestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli.Vet Microbiol. 2011 Nov 21;153(1-2):89-98. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2011.05.023. Epub 2011 Jun 6. Vet Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21680117 Review.
Cited by
-
Bacterial Swarmers Enriched During Intestinal Stress Ameliorate Damage.Gastroenterology. 2021 Jul;161(1):211-224. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.03.017. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Gastroenterology. 2021. PMID: 33741315 Free PMC article.
-
Streptomyces Volatile Compounds Influence Exploration and Microbial Community Dynamics by Altering Iron Availability.mBio. 2019 Mar 5;10(2):e00171-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00171-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30837334 Free PMC article.
-
Apirhabdus apintestini gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of a novel genus of the family Enterobacteriaceae, isolated from the gut of the western honey bee Apis mellifera.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2024 Apr;74(4):006346. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.006346. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38652096 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of the ferric uptake regulator (Fur) protein on pathogenicity in Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliense.PLoS One. 2017 May 17;12(5):e0177647. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177647. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28545065 Free PMC article.
-
The Transcription Factor Lrp of Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii Controls Capsule Production, Motility, and Virulence Important for in planta Growth.Front Microbiol. 2022 Feb 14;12:806504. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.806504. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35237242 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Claflin L. 1999. Compendium of corn diseases, 3rd ed. APS Press, St Paul, MN.
-
- Stewart FC. 1897. A bacterial disease of sweet corn. N Y Agric Exp Station Bull 130:422–439.
-
- Mergaert J, Verdonck L, Kersters K. 1993. Transfer of Erwinia ananas (synonym, Erwinia uredovora) and Erwinia stewartii to the genus Pantoea emend. as Pantoea ananas (Serrano 1928) comb nov. and Pantoea stewartii (Smith 1898) comb nov, respectively, and description of Pantoea stewartii subsp indologenes subsp nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 43:162–173. doi:10.1099/00207713-43-1-162. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

