Ageing and muscular dystrophy differentially affect murine pharyngeal muscles in a region-dependent manner
- PMID: 25326455
- PMCID: PMC4262340
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.280420
Ageing and muscular dystrophy differentially affect murine pharyngeal muscles in a region-dependent manner
Abstract
The inability to swallow, or dysphagia, is a debilitating and life-threatening condition that arises with ageing or disease. Dysphagia results from neurological or muscular impairment of one or more pharyngeal muscles, which function together to ensure proper swallowing and prevent the aspiration of food or liquid into the lungs. Little is known about the effects of age or disease on pharyngeal muscles as a group. Here we show ageing affected pharyngeal muscle growth and atrophy in wild-type mice depending on the particular muscle analysed. Furthermore, wild-type mice also developed dysphagia with ageing. Additionally, we studied pharyngeal muscles in a mouse model for oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy, a dysphagic disease caused by a polyalanine expansion in the RNA binding protein, PABPN1. We examined pharyngeal muscles of mice overexpressing either wild-type A10 or mutant A17 PABPN1. Overexpression of mutant A17 PABPN1 differentially affected growth of the palatopharyngeus muscle dependent on its location within the pharynx. Interestingly, overexpression of wild-type A10 PABPN1 was protective against age-related muscle atrophy in the laryngopharynx and prevented the development of age-related dysphagia. These results demonstrate that pharyngeal muscles are differentially affected by both ageing and muscular dystrophy in a region-dependent manner. These studies lay important groundwork for understanding the molecular and cellular mechanisms that regulate pharyngeal muscle growth and atrophy, which may lead to novel therapies for individuals with dysphagia.
Figures
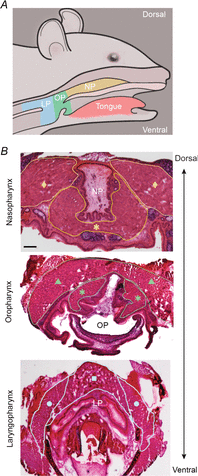



References
-
- Aherne W, Ayyar DR, Clarke PA. Walton JN. Muscle fiber size in normal infants, children and adolescents. An autopsy study. J Neurol Sci. 1971;14:171–182. - PubMed
-
- Aloysius A, Born P, Kinali M, Davis T, Pane M. Mercuri E. Swallowing difficulties in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: indications for feeding assessment and outcome of videofluroscopic swallow studies. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2008;12:239–245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

