Orphan nuclear receptor TR3/Nur77 improves wound healing by upregulating the expression of integrin β4
- PMID: 25326539
- PMCID: PMC4285545
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.14-257550
Orphan nuclear receptor TR3/Nur77 improves wound healing by upregulating the expression of integrin β4
Abstract
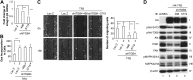
Tissue repair/wound healing, in which angiogenesis plays an important role, is a critical step in many diseases including chronic wound, myocardial infarction, stroke, cancer, and inflammation. Recently, we were the first to report that orphan nuclear receptor TR3/Nur77 is a critical mediator of angiogenesis and its associated microvessel permeability. Tumor growth and angiogenesis induced by VEGF-A, histamine, and serotonin are almost completely inhibited in Nur77 knockout mice. However, it is not known whether TR3/Nur77 plays any roles in wound healing. In these studies, skin wound-healing assay was performed in 3 types of genetically modified mice having various Nur77 activities. We found that ectopic induction of Nur77 in endothelial cells of mice is sufficient to improve skin wound healing. Although skin wound healing in Nur77 knockout mice is comparable to the wild-type control mice, the process is significantly delayed in the EC-Nur77-DN mice, in which a dominant negative Nur77 mutant is inducibly and specifically expressed in mouse endothelial cells. By a loss-of-function assay, we elucidate a novel feed-forward signaling pathway, integrin β4 → PI3K → Akt → FAK, by which TR3 mediates HUVEC migration. Furthermore, TR3/Nur77 regulates the expression of integrin β4 by targeting its promoter activity. In conclusion, expression of TR3/Nur77 improves wound healing by targeting integrin β4. TR3/Nur77 is a potential candidate for proangiogenic therapy. The results further suggest that TR3/Nur77 is required for pathologic angiogenesis but not for developmental/physiologic angiogenesis and that Nur77 and its family members play a redundant role in normal skin wound healing.
Keywords: VEGF; angiogenesis.
© FASEB.
Figures



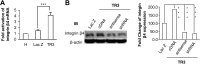
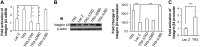
Similar articles
-
Orphan nuclear receptor TR3/Nur77 biologics inhibit tumor growth by targeting angiogenesis and tumor cells.Microvasc Res. 2020 Mar;128:103934. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2019.103934. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Microvasc Res. 2020. PMID: 31654655
-
Orphan nuclear receptor TR3/Nur77 differentially regulates the expression of integrins in angiogenesis.Microvasc Res. 2019 Mar;122:22-33. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2018.10.011. Epub 2018 Nov 1. Microvasc Res. 2019. PMID: 30391133 Free PMC article.
-
DLL4 and Jagged1 are angiogenic targets of orphan nuclear receptor TR3/Nur77.Microvasc Res. 2019 Jul;124:67-75. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2019.03.006. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Microvasc Res. 2019. PMID: 30930165 Free PMC article.
-
Dual roles of orphan nuclear receptor TR3/Nur77/NGFI-B in mediating cell survival and apoptosis.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2014;313:219-58. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800177-6.00007-4. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25376494 Review.
-
Characteristics of Nur77 and its ligands as potential anticancer compounds (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2018 Dec;18(6):4793-4801. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9515. Epub 2018 Sep 27. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 30272297 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pre-mRNA Processing Factor 8 Accelerates the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Regulating the PI3K/Akt Pathway.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 May 26;13:4717-4730. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S241214. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32547101 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphotyrosine profiling of curcumin-induced signaling.Clin Proteomics. 2016 Jun 15;13:13. doi: 10.1186/s12014-016-9114-0. eCollection 2016. Clin Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 27307780 Free PMC article.
-
The role of nuclear hormone receptors in cutaneous wound repair.Cell Biochem Funct. 2015 Jan;33(1):1-13. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3086. Epub 2014 Dec 22. Cell Biochem Funct. 2015. PMID: 25529612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Interactions between NR4A Orphan Nuclear Receptors and NF-κB Are Required for Appropriate Inflammatory Responses and Immune Cell Homeostasis.Biomolecules. 2015 Jun 29;5(3):1302-18. doi: 10.3390/biom5031302. Biomolecules. 2015. PMID: 26131976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NR4A1-3 nuclear receptor activity and immune cell dysregulation in rheumatic diseases.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 22;9:874182. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.874182. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35935773 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Folkman J. (1995) Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat. Med. 1, 27–31 - PubMed
-
- Folkman J. (1996) Fighting cancer by attacking its blood supply. Sci. Am. 275, 150–154 - PubMed
-
- Folkman J. (1997) Angiogenesis and angiogenesis inhibition: an overview. EXS 79, 1–8 - PubMed
-
- Folkman J., D’Amore P. A. (1996) Blood vessel formation: what is its molecular basis? Cell 87, 1153–1155 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

