Emerging molecular phenotypes of asthma
- PMID: 25326577
- PMCID: PMC4338947
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00070.2014
Emerging molecular phenotypes of asthma
Abstract
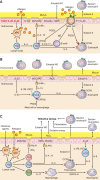
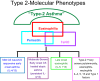
Although asthma has long been considered a heterogeneous disease, attempts to define subgroups of asthma have been limited. In recent years, both clinical and statistical approaches have been utilized to better merge clinical characteristics, biology, and genetics. These combined characteristics have been used to define phenotypes of asthma, the observable characteristics of a patient determined by the interaction of genes and environment. Identification of consistent clinical phenotypes has now been reported across studies. Now the addition of various 'omics and identification of specific molecular pathways have moved the concept of clinical phenotypes toward the concept of molecular phenotypes. The importance of these molecular phenotypes is being confirmed through the integration of molecularly targeted biological therapies. Thus the global term asthma is poised to become obsolete, being replaced by terms that more specifically identify the pathology associated with the disease.
Keywords: Type 2; asthma; endotypes; molecular; phenotypes.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Al-Ramli W, Prefontaine D, Chouiali F, Martin JG, Olivenstein R, Lemiere C, Hamid Q. T(H)17-associated cytokines (IL-17A and IL-17F) in severe asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 123: 1185–1187, 2009. - PubMed
-
- Amelink M, de Groot JC, de Nijs SB, Lutter R, Zwinderman AH, Sterk PJ, ten Brinke A, Bel EH. Severe adult-onset asthma: A distinct phenotype. J Allergy Clin Immunol 132: 336–341, 2013. - PubMed
-
- Amelink M, de Nijs SB, de Groot JC, van Tilburg PM, van Spiegel PI, Krouwels FH, Lutter R, Zwinderman AH, Weersink EJ, ten Brinke A, Sterk PJ, Bel EH. Three phenotypes of adult-onset asthma. Allergy 68: 674–680, 2013. - PubMed
-
- Atherton HC, Jones G, Danahay H. IL-13-induced changes in the goblet cell density of human bronchial epithelial cell cultures: MAP kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 285: L730–L739, 2003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

