Immunohistochemical expression of CD34 and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) in oral submucous fibrosis
- PMID: 25328292
- PMCID: PMC4196280
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-029X.140718
Immunohistochemical expression of CD34 and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) in oral submucous fibrosis
Abstract
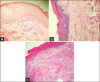
Background: Oral submucous fibrosis (OSMF) is an insidious chronic fibrotic condition that involves the oral mucosa and occasionally the pharynx and esophagus. Vascularity in OSMF has always been a matter of debate. The prevailing concept is that epithelial atrophy occurs due to lack of perfusion but the recent data challenges this concept. Therefore, the present study was conducted to evaluate the immunoreactivity of CD34 and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) in different histological grades of OSMF. This might further shed light to the role of microvasculature in OSMF, so that the epithelial atrophy and resultant malignant transformation seen in the advanced stages might be elucidated.
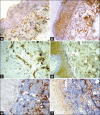
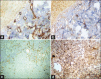
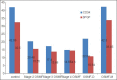
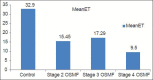
Materials and methods: A total of 30 cases of OSMF were included in the study and mean vascular density (MVD) was calculated using CD34 and bFGF. Five cases of OSMF with dysplasia and 2 cases of OSMF turning malignant were added during the course of the study.
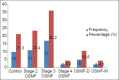
Results: Mean vascular density was found to decrease significantly as the diseases advanced. Furthermore, vascularity increased significantly in cases of OSMF turning towards malignancy.
Conclusion: Our study supports the concept of epithelial atrophy aftermath of lack of perfusion. There is reduced vascularity as the disease advances and this denies the systemic absorption of carcinogens, which affects the already compromised epithelium. Consequently, liberation of angiogenic factors occurs because of malignant transformation, which explains the neoangiogenesis and increased vascularity in OSMF turning towards malignancy. Further studies are required to identify the mechanism leading to carcinogenesis in the atrophied epithelium aftermath of fibrosis and decreased vascularity.
Keywords: CD34; bFGF; oral submucous fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Desai RS, Mamatha GS, Khatri MJ, Shetty SJ. Immunohistochemical expression of CD34 for characterization and quantification of mucosal vasculature and its probable role in malignant transformation of atrophic epithelium in oral submucous fibrosis. Oral Oncol. 2010;46:553–8. - PubMed
-
- Rajendran R, Paul S, Mathews PP, Raghul J, Mohanty M. Characterisation and quantification of mucosal vasculature in oral submucous fibrosis. Indian J Dent Res. 2005;16:83–91. - PubMed
-
- Sabrinath B, Sriram G, Saraswathi TR, Sivapathsundharam B. Immunohistochemical evaluation of mast cells and vascular endothelial proliferation in oral submucous fibrosis. Indian J Dent Res. 2011;22:116–21. - PubMed
-
- Shu-Hui L, Pei-Hsin H, Kuo-Chou C, Su-Hua H, Yi-Shing S. Tumor angiogenesis in oral squamous cell carcinomas: The significance of endothelial markers and hotspot selection. J Med Sci. 2009;29:67–74.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

