X-linked Hyper-IgM Syndrome with Bronchiectasis
- PMID: 25328337
- PMCID: PMC4196358
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-2727.141510
X-linked Hyper-IgM Syndrome with Bronchiectasis
Abstract
The X-linked hyper-immunoglobulin M syndrome (HIGM-1) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by elevated serum IgM levels and low to undetectable levels of serum IgG, IgA and IgE. These patients characteristically present with recurrent sinopulmonary infections and recurrent diarrhea. They also have high susceptibility for Pneumocystis jiroveci (PJ) pneumonia. Herein, we report a case of HGM-1 in a 5-year-old boy who presented with bronchiectasis and, possibly, PJ pneumonia. The diagnosis was established on the basis of clinical features, immune profile, whole blood flow cytometry and history of two male sibling's death due to recurrent pneumonia and diarrhea.
Keywords: Bronchiectasis; Pneumocystis jiroveci; X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome; children.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
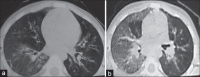
References
-
- Korthäuer U, Graf D, Mages HW, Brière F, Padayachee M, Malcolm S, et al. Defective expression of T-cell CD40 ligand causes X-linked immunodeficiency with hyper-IgM. Nature. 1993;361:539–41. - PubMed
-
- Li AM, Sonnappa S, Lex C, Wong E, Zacharasiewicz A, Bush A, et al. Non-CF bronchiectasis: Does knowing the aetiology lead to changes in management? Eur Respir J. 2005;26:8–14. - PubMed
-
- De Pauw B, Walsh TJ, Donnelly JP, Stevens DA, Edwards JE, Calandra T, et al. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group; National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group. Revised definitions of invasive fungal disease from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46:1813–21. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

