Medical Image Watermarking Technique for Accurate Tamper Detection in ROI and Exact Recovery of ROI
- PMID: 25328515
- PMCID: PMC4190825
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/984646
Medical Image Watermarking Technique for Accurate Tamper Detection in ROI and Exact Recovery of ROI
Abstract
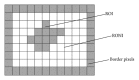
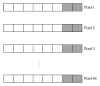
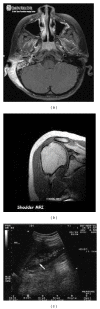
In telemedicine while transferring medical images tampers may be introduced. Before making any diagnostic decisions, the integrity of region of interest (ROI) of the received medical image must be verified to avoid misdiagnosis. In this paper, we propose a novel fragile block based medical image watermarking technique to avoid embedding distortion inside ROI, verify integrity of ROI, detect accurately the tampered blocks inside ROI, and recover the original ROI with zero loss. In this proposed method, the medical image is segmented into three sets of pixels: ROI pixels, region of noninterest (RONI) pixels, and border pixels. Then, authentication data and information of ROI are embedded in border pixels. Recovery data of ROI is embedded into RONI. Results of experiments conducted on a number of medical images reveal that the proposed method produces high quality watermarked medical images, identifies the presence of tampers inside ROI with 100% accuracy, and recovers the original ROI without any loss.
Figures


References
-
- Coatrieux G, Montagner J, Huang H, Roux C. Mixed reversible and RONI watermarking for medical image reliability protection. Proceedings of the 29th Annual International Conference of IEEE-EMBS, Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC '07); August 2007; Lyon, France. pp. 5653–5656. - PubMed
-
- Zain JM, Fauzi ARM. Medical image watermarking with tamper detection and recovery. Proceedings of the 28th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS '06); September 2006; pp. 3270–3273. - PubMed
-
- Liew S-C, Zain JM. Reversible medical image watermarking for tamper detection and recovery. Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE International Conference on Computer Science and Information Technology (ICCSIT '10); July 2010; pp. 417–420.
-
- Liew S-C, Liew S-W, Zain JM. Reversible medical image watermarking for tamper detection and recovery with Run Length Encoding compression. World Academy of Science, Engineering & Technology. 2011;(50):799–803.
-
- Tjokorda Agung BW, Permana FP. Medical image watermarking with tamper detection and recovery using reversible watermarking with LSB modification and Run Length Encoding (RLE) compression. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communication, Networks and Satellite (COMNETSAT '12); July 2012; Bali, Indonesia. pp. 167–171.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

