Fructose induced endotoxemia in pediatric nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease
- PMID: 25328713
- PMCID: PMC4195259
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/560620
Fructose induced endotoxemia in pediatric nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease
Abstract
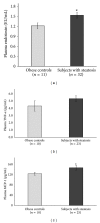
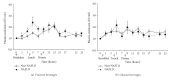
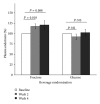
In preclinical studies of fructose-induced NAFLD, endotoxin appears to play an important role. We retrospectively examined samples from three pediatric cohorts (1) to investigate whether endotoxemia is associated with the presence of hepatic steatosis; (2) to evaluate postprandial endotoxin levels in response to fructose beverage in an acute 24-hour feeding challenge, and (3) to determine the change of fasting endotoxin amounts in a 4-week randomized controlled trial comparing fructose to glucose beverages in NAFLD. We found that adolescents with hepatic steatosis had elevated endotoxin levels compared to obese controls and that the endotoxin level correlated with insulin resistance and several inflammatory cytokines. In a 24-hour feeding study, endotoxin levels in NAFLD adolescents increased after fructose beverages (consumed with meals) as compared to healthy children. Similarly, endotoxin was significantly increased after adolescents consumed fructose beverages for 2 weeks and remained high although not significantly at 4 weeks. In conclusion, these data provide support for the concept of low level endotoxemia contributing to pediatric NAFLD and the possible role of fructose in this process. Further studies are needed to determine if manipulation of the microbiome or other methods of endotoxin reduction would be useful as a therapy for pediatric NAFLD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Children with NAFLD are more sensitive to the adverse metabolic effects of fructose beverages than children without NAFLD.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Jul;97(7):E1088-98. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-1370. Epub 2012 Apr 27. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22544914 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Toll-like receptor 4 is involved in the development of fructose-induced hepatic steatosis in mice.Hepatology. 2009 Oct;50(4):1094-104. doi: 10.1002/hep.23122. Hepatology. 2009. PMID: 19637282
-
Fructose as a key player in the development of fatty liver disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Feb 28;19(8):1166-72. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i8.1166. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23482247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary fructose reduction improves markers of cardiovascular disease risk in Hispanic-American adolescents with NAFLD.Nutrients. 2014 Aug 8;6(8):3187-201. doi: 10.3390/nu6083187. Nutrients. 2014. PMID: 25111123 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Carbohydrate intake and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: fructose as a weapon of mass destruction.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2015 Apr;4(2):109-16. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2304-3881.2014.11.05. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26005677 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Precision medicine in alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via modulating the gut microbiota.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016 Dec 1;311(6):G1018-G1036. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00245.2016. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27686615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver Steatosis, Gut-Liver Axis, Microbiome and Environmental Factors. A Never-Ending Bidirectional Cross-Talk.J Clin Med. 2020 Aug 14;9(8):2648. doi: 10.3390/jcm9082648. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32823983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute Intake of Sucrose but Not of the Intense Sweetener Sucralose Is Associated with Post-Prandial Endotoxemia in Healthy Young Adults-A Randomized Controlled Trial.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 18;15(18):4038. doi: 10.3390/nu15184038. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37764821 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Fructose metabolism and its roles in metabolic diseases, inflammatory diseases, and cancer.Mol Biomed. 2025 Jun 23;6(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s43556-025-00287-2. Mol Biomed. 2025. PMID: 40549205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of dietary components on intestinal permeability in health and disease.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020 Nov 1;319(5):G589-G608. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00245.2020. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32902315 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thuy S, Ladurner R, Volynets V, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in humans is associated with increased plasma endotoxin and plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 concentrations and with fructose intake. Journal of Nutrition. 2008;138(8):1452–1455. - PubMed
-
- Verdam FJ, Rensen SS, Driessen A, Greve JW, Buurman WA. Novel evidence for chronic exposure to endotoxin in human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology. 2011;45(2):149–152. - PubMed
-
- Alisi A, Manco M, Devito R, Piemonte F, Nobili V. Endotoxin and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 serum levels associated with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in children. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition. 2010;50(6):645–649. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

