MRI-based Algorithm for Acute Ischemic Stroke Subtype Classification
- PMID: 25328874
- PMCID: PMC4200592
- DOI: 10.5853/jos.2014.16.3.161
MRI-based Algorithm for Acute Ischemic Stroke Subtype Classification
Abstract
Background and purpose: In order to improve inter-rater reliability and minimize diagnosis of undetermined etiology for stroke subtype classification, using a stroke registry, we developed and implemented a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-based algorithm for acute ischemic stroke subtype classification (MAGIC).
Methods: We enrolled patients who experienced an acute ischemic stroke, were hospitalized in the 14 participating centers within 7 days of onset, and had relevant lesions on MR-diffusion weighted imaging (DWI). MAGIC was designed to reflect recent advances in stroke imaging and thrombolytic therapy. The inter-rater reliability was compared with and without MAGIC to classify the Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST) of each stroke patient. MAGIC was then applied to all stroke patients hospitalized since July 2011, and information about stroke subtypes, other clinical characteristics, and stroke recurrence was collected via a web-based registry database.
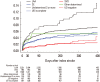
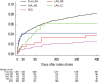
Results: The overall intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) value was 0.43 (95% CI, 0.31-0.57) for MAGIC and 0.28 (95% CI, 0.18-0.42) for TOAST. Large artery atherosclerosis (LAA) was the most common cause of acute ischemic stroke (38.3%), followed by cardioembolism (CE, 22.8%), undetermined cause (UD, 22.2%), and small-vessel occlusion (SVO, 14.6%). One-year stroke recurrence rates were the highest for two or more UDs (11.80%), followed by LAA (7.30%), CE (5.60%), and SVO (2.50%).
Conclusions: Despite several limitations, this study shows that the MAGIC system is feasible and may be helpful to classify stroke subtype in the clinic.
Keywords: Algorithm; Classification; Magnetic resonance imaging; Stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ay H, Furie KL, Singhal A, Smith WS, Sorensen AG, Koroshetz WJ. An evidence-based causative classification system for acute ischemic stroke. Ann Neurol. 2005;58:688–697. - PubMed
-
- Adams HP, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, et al. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke. 1993;24:35–41. - PubMed
-
- Gordon DL, Bendixen BH, Adams HP, Clarke W, Kappelle LJ, Woolson RF The TOAST Investigators. Interphysician agreement in the diagnosis of subtypes of acute ischemic stroke: implications for clinical trials. Neurology. 1993;43:1021–1027. - PubMed
-
- Amarenco P, Bogousslavsky J, Caplan LR, Donnan GA, Hennerici MG. Classification of stroke subtypes. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2009;27:493–501. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

