Axinellamines as broad-spectrum antibacterial agents: scalable synthesis and biology
- PMID: 25328977
- PMCID: PMC4227811
- DOI: 10.1021/ja508632y
Axinellamines as broad-spectrum antibacterial agents: scalable synthesis and biology
Abstract
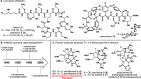
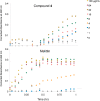
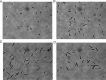
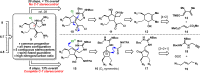
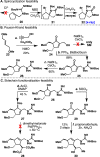
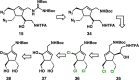
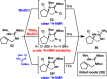
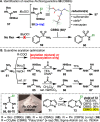
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria present an ongoing challenge to both chemists and biologists as they seek novel compounds and modes of action to out-maneuver continually evolving resistance pathways, especially against Gram-negative strains. The dimeric pyrrole-imidazole alkaloids represent a unique marine natural product class with diverse primary biological activity and chemical architecture. This full account traces the strategy used to develop a second-generation route to key spirocycle 9, culminating in a practical synthesis of the axinellamines and enabling their discovery as broad-spectrum antibacterial agents, with promising activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. While their detailed mode of antibacterial action remains unclear, the axinellamines appear to cause secondary membrane destabilization and impart an aberrant cellular morphology consistent with the inhibition of normal septum formation. This study serves as a rare example of a natural product initially reported to be devoid of biological activity surfacing as an active antibacterial agent with an intriguing mode of action.
Figures

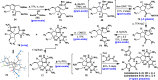
Similar articles
-
Enantioselective total syntheses of (-)-palau'amine, (-)-axinellamines, and (-)-massadines.J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Sep 21;133(37):14710-26. doi: 10.1021/ja2047232. Epub 2011 Aug 23. J Am Chem Soc. 2011. PMID: 21861522 Free PMC article.
-
Facile synthesis of the trans-fused azabicyclo[3.3.0]octane core of the palau'amines and the tricyclic core of the axinellamines from a common intermediate.Org Lett. 2008 Sep 4;10(17):3685-8. doi: 10.1021/ol801289b. Epub 2008 Aug 12. Org Lett. 2008. PMID: 18693745 Free PMC article.
-
Scalable, stereocontrolled total syntheses of (±)-axinellamines A and B.J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Sep 7;133(35):13922-5. doi: 10.1021/ja206191g. Epub 2011 Aug 16. J Am Chem Soc. 2011. PMID: 21846138 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Potentials of Marine Pyrrole-2-Aminoimidazole Alkaloids and their Synthetic Analogs.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018;18(19):1640-1658. doi: 10.2174/1389557516666160505120157. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 27145848 Review.
-
Pharmaceutical Potential of Synthetic and Natural Pyrrolomycins.Molecules. 2015 Dec 4;20(12):21658-71. doi: 10.3390/molecules201219797. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26690095 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Academia-industry symbiosis in organic chemistry.Acc Chem Res. 2015 Mar 17;48(3):712-21. doi: 10.1021/ar500424a. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Acc Chem Res. 2015. PMID: 25702529 Free PMC article.
-
Naturally Occurring Organohalogen Compounds-A Comprehensive Review.Prog Chem Org Nat Prod. 2023;121:1-546. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-26629-4_1. Prog Chem Org Nat Prod. 2023. PMID: 37488466 Review.
-
Screening for antibacterial and cytotoxic activities of Sri Lankan marine sponges through microfractionation: Isolation of bromopyrrole alkaloids from Stylissa massa.PLoS One. 2024 Jan 8;19(1):e0296404. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296404. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38190387 Free PMC article.
-
One-Step Synthesis of 2,5-Diaminoimidazoles and Total Synthesis of Methylglyoxal-Derived Imidazolium Crosslink (MODIC).Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019 Dec 19;58(52):18913-18917. doi: 10.1002/anie.201911156. Epub 2019 Nov 12. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019. PMID: 31713976 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygenated Cyclopentenones via the Pauson-Khand Reaction of Silyl Enol Ether Substrates.Org Lett. 2022 Apr 15;24(14):2750-2755. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.2c00856. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Org Lett. 2022. PMID: 35377671 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Obrecht D.; Bernardini F.; Dale G.; Dembowsky K. Annu. Rep. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 245.
-
- Wright G. D. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 175. - PubMed
-
-
For an editorial commentary describing the ESKAPE pathogens, see:
- Rice L. B. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 1079.and references therein. - PubMed
-
-
- Vaara M. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 571. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

