A loop region in the N-terminal domain of Ebola virus VP40 is important in viral assembly, budding, and egress
- PMID: 25330123
- PMCID: PMC4213565
- DOI: 10.3390/v6103837
A loop region in the N-terminal domain of Ebola virus VP40 is important in viral assembly, budding, and egress
Abstract
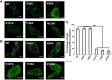
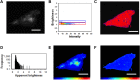
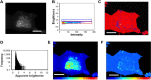
Ebola virus (EBOV) causes viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and can have clinical fatality rates of ~60%. The EBOV genome consists of negative sense RNA that encodes seven proteins including viral protein 40 (VP40). VP40 is the major Ebola virus matrix protein and regulates assembly and egress of infectious Ebola virus particles. It is well established that VP40 assembles on the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane of human cells to regulate viral budding where VP40 can produce virus like particles (VLPs) without other Ebola virus proteins present. The mechanistic details, however, of VP40 lipid-interactions and protein-protein interactions that are important for viral release remain to be elucidated. Here, we mutated a loop region in the N-terminal domain of VP40 (Lys127, Thr129, and Asn130) and find that mutations (K127A, T129A, and N130A) in this loop region reduce plasma membrane localization of VP40. Additionally, using total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy and number and brightness analysis we demonstrate these mutations greatly reduce VP40 oligomerization. Lastly, VLP assays demonstrate these mutations significantly reduce VLP release from cells. Taken together, these studies identify an important loop region in VP40 that may be essential to viral egress.
Figures





References
-
- Feldmann H. Ebola—A growing threat? N. Engl. J. Med. 2014;371:1375–1378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

