The Long-HER study: clinical and molecular analysis of patients with HER2+ advanced breast cancer who become long-term survivors with trastuzumab-based therapy
- PMID: 25330188
- PMCID: PMC4203741
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109611
The Long-HER study: clinical and molecular analysis of patients with HER2+ advanced breast cancer who become long-term survivors with trastuzumab-based therapy
Abstract
Background: Trastuzumab improves survival outcomes in patients with HER2+ metastatic breast cancer. The Long-Her study was designed to identify clinical and molecular markers that could differentiate long-term survivors from patients having early progression after trastuzumab treatment.
Methods: Data were collected from women with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer treated with trastuzumab that experienced a response or stable disease during at least 3 years. Patients having a progression in the first year of therapy with trastuzumab were used as a control. Genes related with trastuzumab resistance were identified and investigated for network and gene functional interrelation. Models predicting poor response to trastuzumab were constructed and evaluated. Finally, a mutational status analysis of selected genes was performed in HER2 positive breast cancer samples.
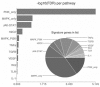
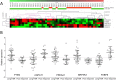
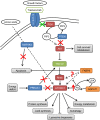
Results: 103 patients were registered in the Long-HER study, of whom 71 had obtained a durable complete response. Median age was 58 years. Metastatic disease was diagnosed after a median of 24.7 months since primary diagnosis. Metastases were present in the liver (25%), lungs (25%), bones (23%) and soft tissues (23%), with 20% of patients having multiple locations of metastases. Median duration of response was 55 months. The molecular analysis included 35 patients from the group with complete response and 18 patients in a control poor-response group. Absence of trastuzumab as part of adjuvant therapy was the only clinical factor associated with long-term survival. Gene ontology analysis demonstrated that PI3K pathway was associated with poor response to trastuzumab-based therapy: tumours in the control group usually had four or five alterations in this pathway, whereas tumours in the Long-HER group had two alterations at most.
Conclusions: Trastuzumab may provide a substantial long-term survival benefit in a selected group of patients. Whole genome expression analysis comparing long-term survivors vs. a control group predicted early progression after trastuzumab-based therapy. Multiple alterations in genes related to the PI3K-mTOR pathway seem to be required to confer resistance to this therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, Fuchs H, Paton V, et al. (2001) Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med 344: 783–792. - PubMed
-
- Burstein HJ, Kuter I, Campos SM, Gelman RS, Tribou L, et al. (2001) Clinical activity of trastuzumab and vinorelbine in women with HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 19: 2722–2730. - PubMed
-
- Marty M, Cognetti F, Maraninchi D, Snyder R, Mauriac L, et al. (2005) Randomized phase II trial of the efficacy and safety of trastuzumab combined with docetaxel in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive metastatic breast cancer administered as first-line treatment: the M77001 study group. J Clin Oncol 23: 4265–4274. - PubMed
-
- Robert N, Leyland-Jones B, Asmar L, Belt R, Ilegbodu D, et al. (2006) Randomized phase III study of trastuzumab, paclitaxel, and carboplatin compared with trastuzumab and paclitaxel in women with HER-2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 24: 2786–2792. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

