The putative signal peptide of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is not required for receptor synthesis but promotes receptor expression
- PMID: 25330813
- PMCID: PMC4240022
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20140120
The putative signal peptide of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is not required for receptor synthesis but promotes receptor expression
Abstract
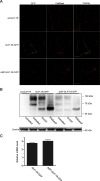
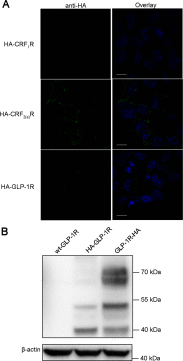
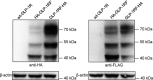
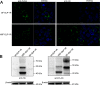
GLP-1R (glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor) mediates the 'incretin effect' and many other anti-diabetic actions of its cognate ligand, GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1). It belongs to the class B family of GPCRs (G protein-coupled receptors) and possesses an N-terminal putative SP (signal peptide). It has been reported that this sequence is required for the synthesis of GLP-1R and is cleaved after receptor synthesis. In the present study, we conducted an in-depth exploration towards the role of the putative SP in GLP-1R synthesis. A mutant GLP-1R without this sequence was expressed in HEK293 cells (human embryonic kidney 293 cells) and displayed normal functionality with respect to ligand binding and activation of adenylate cyclase. Thus the putative SP does not seem to be required for receptor synthesis. Immunoblotting analysis shows that the amount of GLP-1R synthesized in HEK293 cells is low when the putative SP is absent. This indicates that the role of the sequence is to promote the expression of GLP-1R. Furthermore, epitopes tagged at the N-terminal of GLP-1R are detectable by immunofluorescence and immunoblotting in our experiments. In conclusion, the present study points to different roles of SP in GLP-1R expression which broadens our understanding of the functionality of this putative SP of GLP-1R and possibly other Class B GPCRs.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Role of the signal peptide in the synthesis and processing of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Jan;159(1):237-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00517.x. Epub 2009 Nov 27. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20002095 Free PMC article.
-
The regions within the N-terminus critical for human glucagon like peptide-1 receptor (hGLP-1R) cell surface expression.Sci Rep. 2014 Dec 15;4:7410. doi: 10.1038/srep07410. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25502804 Free PMC article.
-
A small molecule ligand of the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor targets its amino-terminal hormone binding domain.J Biol Chem. 2001 Oct 12;276(41):37787-93. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M106692200. Epub 2001 Aug 9. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11498540
-
Minireview: Signal bias, allosterism, and polymorphic variation at the GLP-1R: implications for drug discovery.Mol Endocrinol. 2013 Aug;27(8):1234-44. doi: 10.1210/me.2013-1116. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Mol Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23864649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The structure and function of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor and its ligands.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 May;166(1):27-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01687.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21950636 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 and Its Class B G Protein-Coupled Receptors: A Long March to Therapeutic Successes.Pharmacol Rev. 2016 Oct;68(4):954-1013. doi: 10.1124/pr.115.011395. Pharmacol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27630114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational Peptide Design Cotargeting Glucagon and Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptors.J Chem Inf Model. 2023 Aug 14;63(15):4934-4947. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.3c00752. Epub 2023 Jul 31. J Chem Inf Model. 2023. PMID: 37523325 Free PMC article.
-
Identification, structure modification, and characterization of potential small-molecule SGK3 inhibitors with novel scaffolds.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018 Dec;39(12):1902-1912. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0087-6. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018. PMID: 30038340 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kochl R., Alken M., Rutz C., Krause G., Oksche A., Rosenthal W., Schulein R. The signal peptide of the G protein-coupled human endothelin B receptor is necessary for translocation of the N-terminal tail across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:16131–16138. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111674200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

