Portable and wearable dialysis devices for the treatment of patients with end-stage kidney failure: Wishful thinking or just over the horizon?
- PMID: 25330876
- PMCID: PMC4623087
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-014-2968-3
Portable and wearable dialysis devices for the treatment of patients with end-stage kidney failure: Wishful thinking or just over the horizon?
Abstract
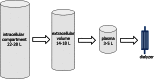
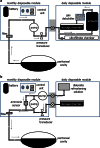
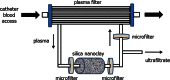
Dialysis is a life-sustaining treatment for patients with end-stage kidney disease. In a different context, for many patients this treatment is the focal point around which their life revolves, not only due to the time spent travelling to and from treatment sessions and the time dedicated to the dialysis treatment itself, but also due to the accompanying dietary and fluid restrictions and medication burden. Wearable and portable dialysis devices could potentially improve patient quality of life by allowing patients to continue with their daily activities of life while undergoing dialysis, as well as by loosening-or removing entirely-dietary and fluid restrictions and reducing pill burden. Advances in nanotechnology manufacturing coupled with advances in electronics and miniaturisation have allowed a new generation of wearable and portable dialysis devices to be developed which are now undergoing large animal and patient clinical trials. We are therefore potentially at a new dawn in the treatment of dialysis patients with the first generation of wearable and portable dialysis devices, which may well revolutionise the treatment and quality of life for patients with end-stage kidney disease.
Keywords: Haemodialysis; Haemofiltration; Peritoneal dialysis; Portable; Wearable.
Figures


References
-
- Davenport A. Membrane designs and composition for hemodialysis, hemofiltration and hemodialfiltration: past, present and future. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2010;62(1):29–40. - PubMed
-
- Jacobsen SC, Stephen RL, Bulloch EC, Luntz RD, Kolf WJ. A wearable artificial kidney: functional description of hardware and clinical results. Proc Clin Dial Transplant Forum. 1975;5:65–71. - PubMed
-
- Stephens RL, Jacobsen SC, Atkin-Thor E, Kolf WJ. A portable wearable artificial kidney (WAK) initial evaluation. Proc Eur Dial Transplant Assoc. 1976;2:511–518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

