Synthesis, characterization, and monoamine transporter activity of the new psychoactive substance 3',4'-methylenedioxy-4-methylaminorex (MDMAR)
- PMID: 25331619
- PMCID: PMC5331736
- DOI: 10.1002/dta.1732
Synthesis, characterization, and monoamine transporter activity of the new psychoactive substance 3',4'-methylenedioxy-4-methylaminorex (MDMAR)
Abstract
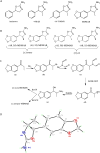
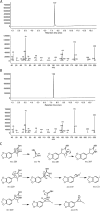
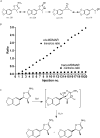
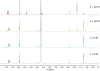
The recent occurrence of deaths associated with the psychostimulant cis-4,4'-dimethylaminorex (4,4'-DMAR) in Europe indicated the presence of a newly emerged psychoactive substance on the market. Subsequently, the existence of 3,4-methylenedioxy-4-methylaminorex (MDMAR) has come to the authors' attention and this study describes the synthesis of cis- and trans-MDMAR followed by extensive characterization by chromatographic, spectroscopic, mass spectrometric platforms and crystal structure analysis. MDMAR obtained from an online vendor was subsequently identified as predominantly the cis-isomer (90%). Exposure of the cis-isomer to the mobile phase conditions (acetonitrile/water 1:1 with 0.1% formic acid) employed for high performance liquid chromatography analysis showed an artificially induced conversion to the trans-isomer, which was not observed when characterized by gas chromatography. Monoamine release activities of both MDMAR isomers were compared with the non-selective monoamine releasing agent (+)-3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) as a standard reference compound. For additional comparison, both cis- and trans-4,4'-DMAR, were assessed under identical conditions. cis-MDMAR, trans-MDMAR, cis-4,4'-DMAR and trans-4,4'-DMAR were more potent than MDMA in their ability to function as efficacious substrate-type releasers at the dopamine (DAT) and norepinephrine (NET) transporters in rat brain tissue. While cis-4,4'-DMAR, cis-MDMAR and trans-MDMAR were fully efficacious releasing agents at the serotonin transporter (SERT), trans-4,4'-DMAR acted as a fully efficacious uptake blocker. Currently, little information is available about the presence of MDMAR on the market but the high potency of ring-substituted methylaminorex analogues at all three monoamine transporters investigated here might be relevant when assessing the potential for serious side-effects after high dose exposure.
Keywords: 4,4′-DMAR; aminorex; forensic; new psychoactive substances; psychostimulants.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures
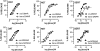
References
-
- EMCDDA–Europol. Joint Reports. Publications Office of the European Union; Luxembourg: 2014. Joint Report on a new psychoactive substance: 4,4′-DMAR (4-methyl-5-(4-methylphenyl)-4,5- dihydrooxazol-2-amine) Available at: http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/attachements.cfm/att_229825_EN_TDAS14006ENN.pdf [21 July 2014]
-
- Cosbey S, Kirk S, McNaul M, Peters L, Prentice B, Quinn A, Elliott SP, Brandt SD, Archer RP. Multiple fatalities involving a new designer drug: para-methyl-4-methylaminorex. J Anal Toxicol. 2014;38:383. - PubMed
-
- Council of the European Union. Request for risk assessment on new psychoactive substance 4,4′-DMAR (4-methyl-5-(4-methylphenyl)-4,5-dihydrooxazol-2-amine) 2014 Available at: http://register.consilium.europa.eu/doc/srv?l=EN&f=ST106192014INIT [21 July 2014]
-
- Davis FT, Brewster ME. A fatality involving U4Euh, a cyclic derivative of phenylpropanolamine. J Forensic Sci. 1988;33:549. - PubMed
-
- Brandt SD, Baumann MH, Partilla JS, Kavanagh PV, Power JD, Talbot B, Twamley B, O’Brien J, Mahony O, Elliott SP, Archer RP, Patrick J, Singh K, Dempster NM, Cosbey SH. Characterization of a novel and potentially lethal designer drug, (±)-cis-para-methyl-4-methylaminorex (4,4′-DMAR, or ’Serotoni’) Drug Test Anal. 2014;6:684. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

