Runt-related transcription factor 2 attenuates the transcriptional activity as well as DNA damage-mediated induction of pro-apoptotic TAp73 to regulate chemosensitivity
- PMID: 25331851
- PMCID: PMC4368372
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.13108
Runt-related transcription factor 2 attenuates the transcriptional activity as well as DNA damage-mediated induction of pro-apoptotic TAp73 to regulate chemosensitivity
Abstract
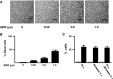
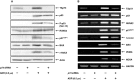
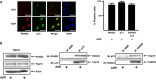
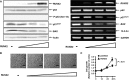
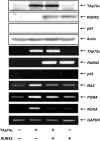
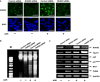
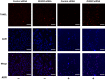
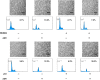
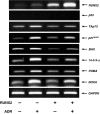
Although runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2) is known to be an essential key transcription factor for osteoblast differentiation and bone formation, RUNX2 also plays a pivotal role in the regulation of p53-dependent DNA damage response. In the present study, we report that, in addition to p53, RUNX2 downregulates pro-apoptotic TAp73 during DNA damage-dependent cell death. Upon adriamycin (ADR) exposure, human osteosarcoma-derived U2OS cells underwent cell death in association with an upregulation of TAp73 and various p53/TAp73-target gene products together with RUNX2. Small interfering RNA-mediated silencing of p73 resulted in a marked reduction in ADR-induced p53/TAp73-target gene expression, suggesting that TAp73 is responsible for the ADR-dependent DNA damage response. Immunoprecipitation and transient transfection experiments demonstrated that RUNX2 forms a complex with TAp73 and impairs its transcriptional activity. Notably, knockdown of RUNX2 stimulated ADR-induced cell death accompanied by a massive induction of TAp73 expression, indicating that RUNX2 downregulates TAp73 expression. Consistent with this notion, the overexpression of RUNX2 suppressed ADR-dependent cell death, which was associated with a remarkable downregulation of TAp73 and p53/TAp73-target gene expression. Collectively, our present findings strongly suggest that RUNX2 attenuates the transcriptional activity and ADR-mediated induction of TAp73, and may provide novel insights into understanding the molecular basis behind the development and/or maintenance of chemoresistance. Thus, we propose that the silencing of RUNX2 might be an attractive strategy for improving the chemosensitivity of malignant cancers.
Keywords: DNA damage; RUNX2; TAp73; cell death; p53.
© 2014 The Authors. FEBS Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of FEBS.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2) inhibits p53-dependent apoptosis through the collaboration with HDAC6 in response to DNA damage.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Apr 25;4(4):e610. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.127. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23618908 Free PMC article.
-
p53 inactivation upregulates p73 expression through E2F-1 mediated transcription.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43564. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043564. Epub 2012 Aug 30. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22952705 Free PMC article.
-
Pml and TAp73 interacting at nuclear body mediate imatinib-induced p53-independent apoptosis of chronic myeloid leukemia cells.Int J Cancer. 2009 Jul 1;125(1):71-7. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24329. Int J Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19291793
-
p73 induces apoptosis by different mechanisms.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005 Jun 10;331(3):713-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.03.156. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005. PMID: 15865927 Review.
-
Impact of RUNX2 on drug-resistant human pancreatic cancer cells with p53 mutations.BMC Cancer. 2018 Mar 20;18(1):309. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4217-9. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29558908 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Silencing of RUNX2 enhances gemcitabine sensitivity of p53-deficient human pancreatic cancer AsPC-1 cells through the stimulation of TAp63-mediated cell death.Cell Death Discov. 2015 Aug 10;1:15010. doi: 10.1038/cddiscovery.2015.10. eCollection 2015. Cell Death Discov. 2015. PMID: 27551445 Free PMC article.
-
Drug resistance-related microRNAs in osteosarcoma: Translating basic evidence into therapeutic strategies.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Apr;23(4):2280-2292. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14064. Epub 2019 Feb 5. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30724027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of RUNX in Hippo Pathway Signaling.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;962:435-448. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-3233-2_26. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28299672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RUNX2 Reverses p53-Induced Chemotherapy Resistance in Gastric Cancer.Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2023 Mar 27;16:253-261. doi: 10.2147/PGPM.S394393. eCollection 2023. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37009416 Free PMC article.
-
Depletion of pro-oncogenic RUNX2 enhances gemcitabine (GEM) sensitivity of p53-mutated pancreatic cancer Panc-1 cells through the induction of pro-apoptotic TAp63.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 1;7(44):71937-71950. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12433. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27713122 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Prives C. Hall PA. The p53 pathway. J Pathol. 1999;187:112–126. &. - PubMed
-
- Sionov RV. Haupt Y. The cellular response to p53: the decision between life and death. Oncogene. 1999;18:6145–6157. &. - PubMed
-
- Vousden KH. Lu X. Live or let die: the cell's response to p53. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:594–604. &. - PubMed
-
- Vogelstein B. Kinzler KW. p53 function and dysfunction. Cell. 1992;70:523–526. &. - PubMed
-
- Harris CC. p53: at the crossroads of molecular carcinogenesis and risk assessment. Science. 1993;262:1980–1981. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

