BIFI: a Taverna plugin for a simplified and user-friendly workflow platform
- PMID: 25332013
- PMCID: PMC4228112
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-740
BIFI: a Taverna plugin for a simplified and user-friendly workflow platform
Abstract
Background: Heterogeneity in the features, input-output behaviour and user interface for available bioinformatics tools and services is still a bottleneck for both expert and non-expert users. Advancement in providing common interfaces over such tools and services are gaining interest among researchers. However, the lack of (meta-) information about input-output data and parameter prevents to provide automated and standardized solutions, which can assist users in setting the appropriate parameters. These limitations must be resolved especially in the workflow-based solution in order to ease the integration of software.
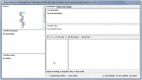
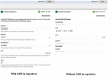
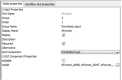
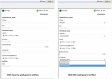
Findings: We report a Taverna Workbench plugin: the XworX BIFI (Beautiful Interfaces for Inputs) implemented as a solution for the aforementioned issues. BIFI provides a Graphical User Interface (GUI) definition language used to layout the user interface and to define parameter options for Taverna workflows. BIFI is also able to submit GUI Definition Files (GDF) directly or discover appropriate instances from a configured repository. In the absence of a GDF, BIFI generates a default interface.
Conclusion: The Taverna Workbench is an open source software providing the ability to combine various services within a workflow. Nevertheless, users can supply input data to the workflow via a simple user interface providing only a text area to enter the input in text form. The workflow may contain meta-information in human readable form such as description text for the port and an example value. However, not all workflow ports are documented so well or have all the required information.BIFI uses custom user interface components for ports which give users feedback on the parameter data type or structure to be used for service execution and enables client-side data validations. Moreover, BIFI offers user interfaces that allow users to interactively construct workflow views and share them with the community, thus significantly increasing usability of heterogeneous, distributed service consumption.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Biowep: a workflow enactment portal for bioinformatics applications.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Mar 8;8 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S19. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-S1-S19. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17430563 Free PMC article.
-
CalcTav--integration of a spreadsheet and Taverna workbench.Bioinformatics. 2011 Sep 15;27(18):2618-9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr425. Epub 2011 Jul 19. Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21775305
-
CDK-Taverna: an open workflow environment for cheminformatics.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Mar 29;11:159. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-159. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20346188 Free PMC article.
-
Web tools for predictive toxicology model building.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2012 Jul;8(7):791-801. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2012.685158. Epub 2012 May 12. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22577953 Review.
-
A guide for integration of proteomic data standards into laboratory workflows.Proteomics. 2013 Feb;13(3-4):480-92. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201200268. Epub 2013 Jan 15. Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23319203 Review.
References
-
- Li P, Castrillo JI, Velarde G, Wassink I, Soiland-Reyes S, Owen S, Withers D, Oinn T, Pocock MR, Goble C, Oliver SG, Kell DB. Performing statistical analyses on quantitative data in Taverna workflows: an example using R and maxdBrowse to identify differentially-expressed genes from microarray data. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008;9:334. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-334. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Web Services Activity Statement. [http://www.w3.org/2002/ws/Activity]
-
- Web Services Description Language (WSDL) Version 2.0 Part 1: Core Language. http://www.w3.org/TR/wsdl20/
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

