Defect dynamics in active nematics
- PMID: 25332389
- PMCID: PMC4223672
- DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2013.0365
Defect dynamics in active nematics
Abstract
Topological defects are distinctive signatures of liquid crystals. They profoundly affect the viscoelastic behaviour of the fluid by constraining the orientational structure in a way that inevitably requires global changes not achievable with any set of local deformations. In active nematic liquid crystals, topological defects not only dictate the global structure of the director, but also act as local sources of motion, behaving as self-propelled particles. In this article, we present a detailed analytical and numerical study of the mechanics of topological defects in active nematic liquid crystals.
Keywords: active liquid crystals; chaotic dynamics; self-propelled particles; topological defects.
© 2014 The Author(s) Published by the Royal Society. All rights reserved.
Figures

 . The unstable regions are bounded by the critical activity given in equation (2.5). Flow tumbling extensile nematic with |λ|<1 are unstable to bend when active stresses are extensile (α<0) and to splay when active stresses are contractile (α>0). Conversely, strongly flow aligning (|λ|≫1) is unstable to splay when active stresses are extensile (α<0) and to bend when active stresses are contractile (α>0). (Online version in colour.)
. The unstable regions are bounded by the critical activity given in equation (2.5). Flow tumbling extensile nematic with |λ|<1 are unstable to bend when active stresses are extensile (α<0) and to splay when active stresses are contractile (α>0). Conversely, strongly flow aligning (|λ|≫1) is unstable to splay when active stresses are extensile (α<0) and to bend when active stresses are contractile (α>0). (Online version in colour.)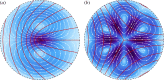
 (a) and
(a) and  (b) disclination. The solid red lines are tangent to the director field
(b) disclination. The solid red lines are tangent to the director field  with θd=kϕ and
with θd=kϕ and  . The background shows the active backflow associated with the disclinations and obtained by solving the Stokes equation (3.6) with no-slip boundary conditions on a circle (dashed black line). The intensity of the background colour is proportional to the magnitude of the flow velocity. The white streamlines are given by equation (3.9). (Online version in colour.)
. The background shows the active backflow associated with the disclinations and obtained by solving the Stokes equation (3.6) with no-slip boundary conditions on a circle (dashed black line). The intensity of the background colour is proportional to the magnitude of the flow velocity. The white streamlines are given by equation (3.9). (Online version in colour.)
 . In the bottom panel, the colour denotes the magnitude of the concentration c relative to the average value c0=2c⋆. Depending on the sign of α, the backflow tends to speed up (α>0) or slow down (α<0) the annihilation process by increasing or decreasing the velocity of the
. In the bottom panel, the colour denotes the magnitude of the concentration c relative to the average value c0=2c⋆. Depending on the sign of α, the backflow tends to speed up (α>0) or slow down (α<0) the annihilation process by increasing or decreasing the velocity of the  disclination. For α negative and sufficiently large in magnitude, the
disclination. For α negative and sufficiently large in magnitude, the  defect reverses its direction of motion (d) and escapes annihilation. (Online version in colour.)
defect reverses its direction of motion (d) and escapes annihilation. (Online version in colour.)
 disclinations self-propel in the direction of their ‘tail’ (contractile) or ‘head’ (extensile). Based on the mutual orientation of the defects, this can lead to an attractive or repulsive interaction. (Online version in colour.)
disclinations self-propel in the direction of their ‘tail’ (contractile) or ‘head’ (extensile). Based on the mutual orientation of the defects, this can lead to an attractive or repulsive interaction. (Online version in colour.)
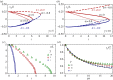
 defects with the relative orientation shown in figure 3 and separation L/2. (a) Defect trajectories for γ=5 and various α values (indicated in the plot). The upper (red) and lower (blue) curves correspond to the positive and negative disclination, respectively. The defects annihilate where the two curves merge. (b) The same plot for γ=10. Slowing down the relaxational dynamics of the nematic phase increases the annihilation time and for α=−0.8 reverses the direction of motion of the
defects with the relative orientation shown in figure 3 and separation L/2. (a) Defect trajectories for γ=5 and various α values (indicated in the plot). The upper (red) and lower (blue) curves correspond to the positive and negative disclination, respectively. The defects annihilate where the two curves merge. (b) The same plot for γ=10. Slowing down the relaxational dynamics of the nematic phase increases the annihilation time and for α=−0.8 reverses the direction of motion of the  disclination. (c) Defect separation as a function of time for α=0.8 and various γ values. (d) Annihilation time normalized by the corresponding annihilation time obtained at α=0 (i.e.
disclination. (c) Defect separation as a function of time for α=0.8 and various γ values. (d) Annihilation time normalized by the corresponding annihilation time obtained at α=0 (i.e.  ). The line is a fit to
). The line is a fit to  with ta given by equation (4.6). As described in the text this expression only depends on the dimensionless parameter
with ta given by equation (4.6). As described in the text this expression only depends on the dimensionless parameter  . The fit is obtained with
. The fit is obtained with  . (Online version in colour.)
. (Online version in colour.)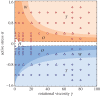

 and
and  disclinations respectively. The dotted blue line for α=−1.2 corresponds to the turbulent regime in which defects proliferate: (h), (i) and (j). In all the snapshots, the background colours are set by the magnitude of the vorticity ω and the order parameter S rescaled by the equilibrium value
disclinations respectively. The dotted blue line for α=−1.2 corresponds to the turbulent regime in which defects proliferate: (h), (i) and (j). In all the snapshots, the background colours are set by the magnitude of the vorticity ω and the order parameter S rescaled by the equilibrium value  , whereas the solid lines indicate velocity (top) and director field (bottom). Movies displaying the time evolution of each state are included as the electronic supplementary material. (Online version in colour.)
, whereas the solid lines indicate velocity (top) and director field (bottom). Movies displaying the time evolution of each state are included as the electronic supplementary material. (Online version in colour.)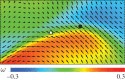
 (filled circle) and a
(filled circle) and a  (open triangle) defect pair along a wall or α=−0.8 and γ=20. The black arrows indicate the flow velocity, while the background colour is related with the local vorticity. The wall is also the boundary between a pair of vortices of opposite circulation. The flow field of opposite-signed vortices adds at the wall, yielding a region of high shear that promotes defect unbinding. (Online version in colour.)
(open triangle) defect pair along a wall or α=−0.8 and γ=20. The black arrows indicate the flow velocity, while the background colour is related with the local vorticity. The wall is also the boundary between a pair of vortices of opposite circulation. The flow field of opposite-signed vortices adds at the wall, yielding a region of high shear that promotes defect unbinding. (Online version in colour.)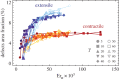
Similar articles
-
Synthetic Active Liquid Crystals Powered by Acoustic Waves.Adv Mater. 2025 May;37(19):e2418846. doi: 10.1002/adma.202418846. Epub 2025 Mar 26. Adv Mater. 2025. PMID: 40135350 Free PMC article.
-
Defect annihilation and proliferation in active nematics.Phys Rev Lett. 2013 May 31;110(22):228101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.228101. Epub 2013 May 29. Phys Rev Lett. 2013. PMID: 23767749
-
Orientational order of motile defects in active nematics.Nat Mater. 2015 Nov;14(11):1110-5. doi: 10.1038/nmat4387. Epub 2015 Aug 17. Nat Mater. 2015. PMID: 26280224 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Tissues as Active Nematic Liquid Crystals.Adv Mater. 2018 Nov;30(47):e1802579. doi: 10.1002/adma.201802579. Epub 2018 Aug 29. Adv Mater. 2018. PMID: 30156334 Review.
-
Spontaneous flow created by active topological defects.Eur Phys J E Soft Matter. 2022 Apr 7;45(4):30. doi: 10.1140/epje/s10189-022-00186-2. Eur Phys J E Soft Matter. 2022. PMID: 35389081 Review.
Cited by
-
Wrinkling Instability in 3D Active Nematics.Nano Lett. 2020 Sep 9;20(9):6281-6288. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c01546. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Nano Lett. 2020. PMID: 32786934 Free PMC article.
-
Edges impose planar alignment in nematic monolayers by directing cell elongation and enhancing migration.Soft Matter. 2018 Sep 7;14(33):6867-6874. doi: 10.1039/c8sm00612a. Epub 2018 Aug 6. Soft Matter. 2018. PMID: 30079410 Free PMC article.
-
Tunable structure and dynamics of active liquid crystals.Sci Adv. 2018 Oct 12;4(10):eaat7779. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aat7779. eCollection 2018 Oct. Sci Adv. 2018. PMID: 30333990 Free PMC article.
-
Mesoscopic simulations of active nematics.Sci Adv. 2022 Aug 26;8(34):eabo5788. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abo5788. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36001669 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic Active Liquid Crystals Powered by Acoustic Waves.Adv Mater. 2025 May;37(19):e2418846. doi: 10.1002/adma.202418846. Epub 2025 Mar 26. Adv Mater. 2025. PMID: 40135350 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marchetti MC, Joanny JF, Ramaswamy S, Liverpool TB, Prost J, Rao M, Simha RA. 2013. Hydrodynamics of soft active matter. Rev. Mod. Phys. 85, 1143–1189. (10.1103/RevModPhys.85.1143) - DOI
-
- Voituriez R, Joanny JF, Prost J. 2005. Spontaneous flow transition in active polar gels. Europhys. Lett. 70, 404–410. (10.1209/epl/i2004-10501-2) - DOI
-
- Ramaswamy S, Simha RA, Toner J. 2003. Active nematics on a substrate: giant number fluctuations and long-time tails. Europhys. Lett. 62, 196–202. (10.1209/epl/i2003-00346-7) - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

