Does the method of weight loss effect long-term changes in weight, body composition or chronic disease risk factors in overweight or obese adults? A systematic review
- PMID: 25333384
- PMCID: PMC4198137
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109849
Does the method of weight loss effect long-term changes in weight, body composition or chronic disease risk factors in overweight or obese adults? A systematic review
Abstract
Background: Differences in biological changes from weight loss by energy restriction and/or exercise may be associated with differences in long-term weight loss/regain.
Objective: To assess the effect of weight loss method on long-term changes in weight, body composition and chronic disease risk factors.
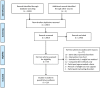
Data sources: PubMed and Embase were searched (January 1990-October 2013) for studies with data on the effect of energy restriction, exercise (aerobic and resistance) on long-term weight loss. Twenty articles were included in this review.
Study eligibility criteria: Primary source, peer reviewed randomized trials published in English with an active weight loss period of >6 months, or active weight loss with a follow-up period of any duration, conducted in overweight or obese adults were included.
Study appraisal and synthesis methods: Considerable heterogeneity across trials existed for important study parameters, therefore a meta-analysis was considered inappropriate. Results were synthesized and grouped by comparisons (e.g. diet vs. aerobic exercise, diet vs. diet + aerobic exercise etc.) and study design (long-term or weight loss/follow-up).
Results: Forty percent of trials reported significantly greater long-term weight loss with diet compared with aerobic exercise, while results for differences in weight regain were inconclusive. Diet+aerobic exercise resulted in significantly greater weight loss than diet alone in 50% of trials. However, weight regain (∼ 55% of loss) was similar in diet and diet+aerobic exercise groups. Fat-free mass tended to be preserved when interventions included exercise.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Donato K, Pi-Sunyer F, Becker D, Bouchard C, Carleton R, et al. (1998) Executive summary of the clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults. Archives of Internal Medicine 158: 1855–1867. - PubMed
-
- Meckling KA, O'Sullivan C, Saari D (2004) Comparison of a low-fat diet to a low-carbohydrate diet on weight loss, body composition, and risk factors for diabetes and cardiovascular disease in free-living, overweight men and women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89: 2717–2723. - PubMed
-
- Rosenkilde M, Auerbach P, Reichkendler MH, Ploug T, Stallknecht BM, et al. (2012) Body fat loss and compensatory mechanisms in response to different doses of aerobic exercise—a randomized controlled trial in overweight sedentary males. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 303: R571–579. - PubMed
-
- Ross R, Dagnone D, Jones PJH, Smith H, Paddags A, et al. (2000) Reduction in obesity and related comorbid conditions after diet-induced weight loss or exercise -induced weight loss in men: A randomized, controlled trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 133: 92–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases