Favipiravir elicits antiviral mutagenesis during virus replication in vivo
- PMID: 25333492
- PMCID: PMC4204012
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03679
Favipiravir elicits antiviral mutagenesis during virus replication in vivo
Abstract
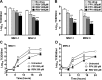
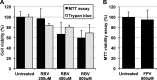
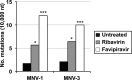
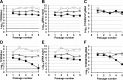
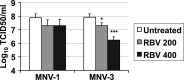
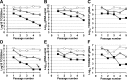
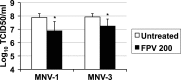
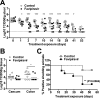
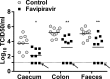
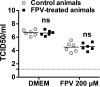
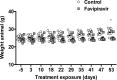
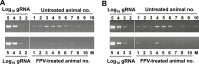
Lethal mutagenesis has emerged as a novel potential therapeutic approach to treat viral infections. Several studies have demonstrated that increases in the high mutation rates inherent to RNA viruses lead to viral extinction in cell culture, but evidence during infections in vivo is limited. In this study, we show that the broad-range antiviral nucleoside favipiravir reduces viral load in vivo by exerting antiviral mutagenesis in a mouse model for norovirus infection. Increased mutation frequencies were observed in samples from treated mice and were accompanied with lower or in some cases undetectable levels of infectious virus in faeces and tissues. Viral RNA isolated from treated animals showed reduced infectivity, a feature of populations approaching extinction during antiviral mutagenesis. These results suggest that favipiravir can induce norovirus mutagenesis in vivo, which in some cases leads to virus extinction, providing a proof-of-principle for the use of favipiravir derivatives or mutagenic nucleosides in the clinical treatment of noroviruses.
Keywords: error-catastrophe; favipiravir; infectious disease; lethal mutagenesis; microbiology; norovirus; polymerase fidelity; quasispecies; viruses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures


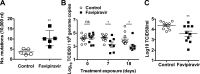
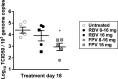
References
-
- Agudo R, Ferrer-Orta C, Arias A, de la Higuera I, Perales C, Pérez-Luque R, Verdaguer N, Domingo E. 2010. A multi-step process of viral adaptation to a mutagenic nucleoside analogue by modulation of transition types leads to extinction-escape. PLoS Pathogens 6:e1001072. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001072 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Asahina Y, Izumi N, Enomoto N, Uchihara M, Kurosaki M, Onuki Y, Nishimura Y, Ueda K, Tsuchiya K, Nakanishi H, Kitamura T, Miyake S. 2005. Mutagenic effects of ribavirin and response to interferon/ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C. Journal of Hepatology 43:623–629. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2005.05.032 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

