Expression of the IL-7 receptor alpha-chain is down regulated on the surface of CD4 T-cells by the HIV-1 Tat protein
- PMID: 25333710
- PMCID: PMC4205093
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111193
Expression of the IL-7 receptor alpha-chain is down regulated on the surface of CD4 T-cells by the HIV-1 Tat protein
Abstract
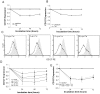
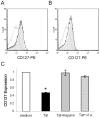
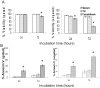
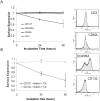
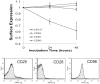
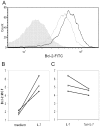
HIV infection elicits defects in CD4 T-cell homeostasis in both a quantitative and qualitative manner. Interleukin-7 (IL-7) is essential to T-cell homeostasis and several groups have shown reduced levels of the IL-7 receptor alpha-chain (CD127) on both CD4 and CD8 T-cells in viremic HIV+ patients. We have shown previously that soluble HIV Tat protein specifically down regulates cell surface expression of CD127 on human CD8 T-cells in a paracrine fashion. The effects of Tat on CD127 expression in CD4 T-cells has yet to be described. To explore this effect, CD4 T-cells were isolated from healthy individuals and expression levels of CD127 were examined on cells incubated in media alone or treated with Tat protein. We show here that, similar to CD8 T-cells, the HIV-1 Tat protein specifically down regulates CD127 on primary human CD4 T-cells and directs the receptor to the proteasome for degradation. Down regulation of CD127 in response to Tat was seen on both memory and naive CD4 T-cell subsets and was blocked using either heparin or anti-Tat antibodies. Tat did not induce apoptosis in cultured primary CD4 T-cells over 72 hours as determined by Annexin V and PI staining. Pre-incubation of CD4 T-cells with HIV-1 Tat protein did however reduce the ability of IL-7 to up regulate Bcl-2 expression. Similar to exogenous Tat, endogenously expressed HIV Tat protein also suppressed CD127 expression on primary CD4 T-cells. In view of the important role IL-7 plays in lymphocyte proliferation, homeostasis and survival, down regulation of CD127 by Tat likely plays a central role in immune dysregulation and CD4 T-cell decline. Understanding this effect could lead to new approaches to mitigate the CD4 T-cell loss evident in HIV infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
IL-7 and the HIV Tat protein act synergistically to down-regulate CD127 expression on CD8 T cells.Int Immunol. 2009 Mar;21(3):203-16. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxn140. Epub 2009 Jan 15. Int Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19147839
-
IL-7 receptor recovery on CD8 T-cells isolated from HIV+ patients is inhibited by the HIV Tat protein.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 17;9(7):e102677. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102677. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25033393 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble HIV Tat protein removes the IL-7 receptor alpha-chain from the surface of resting CD8 T cells and targets it for degradation.J Immunol. 2010 Sep 1;185(5):2854-66. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902207. Epub 2010 Jul 26. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20660706
-
The influence of HIV on CD127 expression and its potential implications for IL-7 therapy.Semin Immunol. 2012 Jun;24(3):231-40. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2012.02.006. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Semin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22421574 Review.
-
Blocking Formation of the Stable HIV Reservoir: A New Perspective for HIV-1 Cure.Front Immunol. 2019 Aug 22;10:1966. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01966. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31507594 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PLA2G1B is involved in CD4 anergy and CD4 lymphopenia in HIV-infected patients.J Clin Invest. 2020 Jun 1;130(6):2872-2887. doi: 10.1172/JCI131842. J Clin Invest. 2020. PMID: 32436864 Free PMC article.
-
Double-Negative T-Cells during Acute Human Immunodeficiency Virus and Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Infections and Following Early Antiretroviral Therapy Initiation.Viruses. 2024 Oct 14;16(10):1609. doi: 10.3390/v16101609. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39459942 Free PMC article.
-
TMPRSS13 promotes cell survival, invasion, and resistance to drug-induced apoptosis in colorectal cancer.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 17;10(1):13896. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70636-4. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32807808 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chun TW, Carruth L, Finzi D, Shen X, DiGiuseppe JA, et al. (1997) Quantification of latent tissue reservoirs and total body viral load in HIV-1 infection. Nature 387: 183–188. - PubMed
-
- Clark DR, de Boer RJ, Wolthers KC, Miedema F (1999) T cell dynamics in HIV-1 infection. Adv Immunol 73: 301–327. - PubMed
-
- Hazenberg MD, Hamann D, Schuitemaker H, Miedema F (2000) T cell depletion in HIV-1 infection: how CD4+ T cells go out of stock. Nat Immunol 1: 285–289. - PubMed
-
- McCune JM (2001) The dynamics of CD4+ T-cell depletion in HIV disease. Nature 410: 974–979. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

