Ciliopathy proteins establish a bipartite signaling compartment in a C. elegans thermosensory neuron
- PMID: 25335890
- PMCID: PMC4265742
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.157610
Ciliopathy proteins establish a bipartite signaling compartment in a C. elegans thermosensory neuron
Abstract
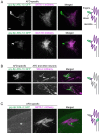
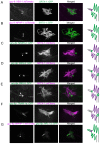
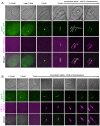
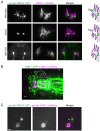
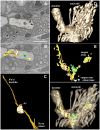
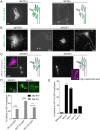
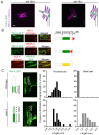
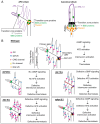
How signaling domains form is an important, yet largely unexplored question. Here, we show that ciliary proteins help establish two contiguous, yet distinct cyclic GMP (cGMP) signaling compartments in Caenorhabditis elegans thermosensory AFD neurons. One compartment, a bona fide cilium, is delineated by proteins associated with Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS), Meckel syndrome and nephronophthisis at its base, and requires NPHP-2 (known as inversin in mammals) to anchor a cGMP-gated ion channel within the proximal ciliary region. The other, a subcompartment with profuse microvilli and a different lipid environment, is separated from the dendrite by a cellular junction and requires BBS-8 and DAF-25 (known as Ankmy2 in mammals) for correct localization of guanylyl cyclases needed for thermosensation. Consistent with a requirement for a membrane diffusion barrier at the subcompartment base, we reveal the unexpected presence of ciliary transition zone proteins where no canonical transition zone ultrastructure exists. We propose that differential compartmentalization of signal transduction components by ciliary proteins is important for the functions of ciliated sensory neurons.
Keywords: Compartmentalization; Primary cilia; Sensory neuron; Thermotaxis; Transition zone; cGMP signaling.
© 2014. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mutations in a guanylate cyclase GCY-35/GCY-36 modify Bardet-Biedl syndrome-associated phenotypes in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Genet. 2011 Oct;7(10):e1002335. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002335. Epub 2011 Oct 13. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 22022287 Free PMC article.
-
A novel zf-MYND protein, CHB-3, mediates guanylyl cyclase localization to sensory cilia and controls body size of Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Genet. 2010 Nov 24;6(11):e1001211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001211. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 21124861 Free PMC article.
-
Active transport and diffusion barriers restrict Joubert Syndrome-associated ARL13B/ARL-13 to an Inv-like ciliary membrane subdomain.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(12):e1003977. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003977. Epub 2013 Dec 5. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 24339792 Free PMC article.
-
The tubulin code specializes neuronal cilia for extracellular vesicle release.Dev Neurobiol. 2021 Apr;81(3):231-252. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22787. Epub 2020 Nov 8. Dev Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 33068333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Membrane-Bound Guanylyl Cyclases within the Ciliary Compartment.Biochemistry. 2025 Aug 5;64(15):3165-3172. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5c00326. Epub 2025 Jul 21. Biochemistry. 2025. PMID: 40689462 Review.
Cited by
-
The nphp-2 and arl-13 genetic modules interact to regulate ciliogenesis and ciliary microtubule patterning in C. elegans.PLoS Genet. 2014 Dec 11;10(12):e1004866. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004866. eCollection 2014 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 25501555 Free PMC article.
-
Ectocytosis prevents accumulation of ciliary cargo in C. elegans sensory neurons.Elife. 2021 Sep 17;10:e67670. doi: 10.7554/eLife.67670. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34533135 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans PPEF-type phosphatase (Retinal degeneration C ortholog) functions in diverse classes of cilia to regulate nematode behaviors.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 16;14(1):28347. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79057-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39550471 Free PMC article.
-
ROS and cGMP signaling modulate persistent escape from hypoxia in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Biol. 2022 Jun 21;20(6):e3001684. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001684. eCollection 2022 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2022. PMID: 35727855 Free PMC article.
-
Ciliary subcompartments: how are they established and what are their functions?BMB Rep. 2015 Jul;48(7):380-7. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2015.48.7.084. BMB Rep. 2015. PMID: 25936781 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aveldaño M. I., Bazán N. G. (1983). Molecular species of phosphatidylcholine, -ethanolamine, -serine, and -inositol in microsomal and photoreceptor membranes of bovine retina. J. Lipid Res. 24, 620–627. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

