Plasmonic nanodiamonds: targeted core-shell type nanoparticles for cancer cell thermoablation
- PMID: 25336437
- PMCID: PMC4411186
- DOI: 10.1002/adhm.201400421
Plasmonic nanodiamonds: targeted core-shell type nanoparticles for cancer cell thermoablation
Abstract
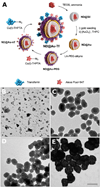
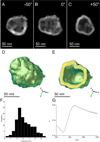
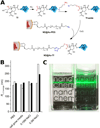
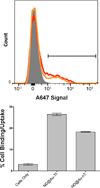
Targeted biocompatible nanostructures with controlled plasmonic and morphological parameters are promising materials for cancer treatment based on selective thermal ablation of cells. Here, core-shell plasmonic nanodiamonds consisting of a silica-encapsulated diamond nanocrystal coated in a gold shell are designed and synthesized. The architecture of particles is analyzed and confirmed in detail using electron tomography. The particles are biocompatibilized using a PEG polymer terminated with bioorthogonally reactive alkyne groups. Azide-modified transferrin is attached to these particles, and their high colloidal stability and successful targeting to cancer cells overexpressing the transferrin receptor are demonstrated. The particles are nontoxic to the cells and they are readily internalized upon binding to the transferrin receptor. The high plasmonic cross section of the particles in the near-infrared region is utilized to quantitatively ablate the cancer cells with a short, one-minute irradiation by a pulse 750-nm laser.
Keywords: ablation; cancer; gold; nanodiamonds; plasmonics.
© 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures

References
-
- Khlebtsov NG, Dykman LA. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2010;111:1.
-
- Jones MR, Osberg KD, Macfarlane RJ, Langille MR, Mirkin CA. Chem. Rev. 2011;111:3736. - PubMed
-
- Daniel MC, Astruc D. Chem. Rev. 2004;104:293. - PubMed
-
- Henry A-I, Bingham JM, Ringe E, Marks LD, Schatz GC, Van Duyne RP. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2011;115:9291.
-
- Agrawal A, Huang S, Wei Haw Lin A, Barton JK, Drezek RA, Pfefer TJ, Lee M-H. J. Biomed. Opt. 2006;11:041121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

