Enhancing Mother Infant Interactions through Video Feedback Enabled Interventions in Women with Schizophrenia: A Single Subject Research Design Study
- PMID: 25336768
- PMCID: PMC4201788
- DOI: 10.4103/0253-7176.140702
Enhancing Mother Infant Interactions through Video Feedback Enabled Interventions in Women with Schizophrenia: A Single Subject Research Design Study
Abstract
Background: It has been shown that mother infant interactions are often impaired in mothers with schizophrenia. Contributory factors include psychotic symptoms, negative symptoms and surrogate parenting by others.
Aim: This study describes the effectiveness of video feedback in enhancing mother-infant interaction in mothers with schizophrenia who have impaired interaction with their infant.
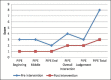
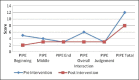
Materials and methods: Two women with schizophrenia who were admitted for persistent psychotic symptoms and poor mothering skills, participated in the intervention. Pre intervention parenting assessment was done using video recording of mother infant interaction. Six sessions of mothering intervention were provided using video feedback and a repeat recording was done. Pre-and post-intervention videos were subsequently rated in a blind fashion by an independent expert in perinatal psychiatry using the pediatric infant parent exam (PIPE) scale.
Results: Pre and post intervention comparison of PIPE scores indicating significant improvement in several areas of mothering.
Conclusions: Video feedback is a simple and inexpensive tool which can be used for improving mothering skills among mothers with postpartum psychosis or schizophrenia even in low resource settings.
Keywords: Mother infant interaction; postpartum psychosis; schizophrenia; video feedback.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Use of video feedback intervention in an inpatient perinatal psychiatric setting to improve maternal parenting.Arch Womens Ment Health. 2012 Aug;15(4):249-57. doi: 10.1007/s00737-012-0283-1. Epub 2012 May 16. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2012. PMID: 22588508 Clinical Trial.
-
Listening to the Voices of Mothers Who Participated in a Video Feedback Intervention for Postpartum Depression.Glob Qual Nurs Res. 2024 Apr 15;11:23333936241245588. doi: 10.1177/23333936241245588. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Glob Qual Nurs Res. 2024. PMID: 38628401 Free PMC article.
-
Promising Results From a Video-Feedback Interaction Guidance Intervention for Improving Maternal-Infant Interaction Quality of Depressed Mothers: A Feasibility Pilot Study.Can J Nurs Res. 2020 Jun;52(2):74-87. doi: 10.1177/0844562119892769. Epub 2020 Jan 7. Can J Nurs Res. 2020. PMID: 31910674
-
Mothers with acute and chronic postpartum psychoses and impact on the mother-infant interaction.Schizophr Res. 2018 Jul;197:45-58. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2018.02.032. Epub 2018 Feb 26. Schizophr Res. 2018. PMID: 29496331
-
A review of mother-child relational interventions and their usefulness for mothers with schizophrenia.Arch Womens Ment Health. 2008 Jul;11(3):171-9. doi: 10.1007/s00737-008-0010-0. Epub 2008 May 21. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2008. PMID: 18493714 Review.
Cited by
-
Mother's Emotional and Posttraumatic Reactions after a Preterm Birth: The Mother-Infant Interaction Is at Stake 12 Months after Birth.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 29;11(3):e0151091. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151091. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27022953 Free PMC article.
-
Through babies' eyes: Practical and theoretical considerations of using wearable technology to measure parent-infant behaviour from the mothers' and infants' view points.Infant Behav Dev. 2017 May;47:62-71. doi: 10.1016/j.infbeh.2017.02.006. Epub 2017 Mar 25. Infant Behav Dev. 2017. PMID: 28347907 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes for women admitted to a mother and baby unit: a systematic review.Int J Womens Health. 2015 Apr 30;7:459-76. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S69472. eCollection 2015. Int J Womens Health. 2015. PMID: 25995650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The establishment of a mother-baby inpatient psychiatry unit in India: Adaptation of a Western model to meet local cultural and resource needs.Indian J Psychiatry. 2015 Jul-Sep;57(3):290-4. doi: 10.4103/0019-5545.166621. Indian J Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26600584 Free PMC article.
-
Bonding and Infants' Development and Quality of Life: A Study Among Mothers with Severe Mental Illnesses in Remission.Indian J Psychol Med. 2023 May;45(3):250-256. doi: 10.1177/02537176231164732. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Indian J Psychol Med. 2023. PMID: 37152397 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sharma V, Murthy S, Agarwal M, Wilkinson G. Comparison of people with schizophrenia from Liverpool, England and Sakalwara, Bangalore. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 1998;44:225–30.
-
- Abel KM, Webb RT, Salmon MP, Wan MW, Appleby L. Prevalence and predictors of parenting outcomes in a cohort of mothers with schizophrenia admitted for joint mother and baby psychiatric care in England. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;66:781–9. - PubMed
-
- Seneviratne G, Conroy S, Marks M. Parenting assessment in a psychiatric mother and baby unit. Br J Soc Work. 2003;33:535–55.
-
- Montag C, Heinz A, Kunz D, Gallinat J. Self-reported empathic abilities in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2007;92:85–9. - PubMed
-
- van ’t Wout M, Aleman A, Kessels RP, Cahn W, de Haan EH, Kahn RS. Exploring the nature of facial affect processing deficits in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2007;150:227–35. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources